- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Electrode position, AP or AL, may not impact success rate of cardioversion of AF
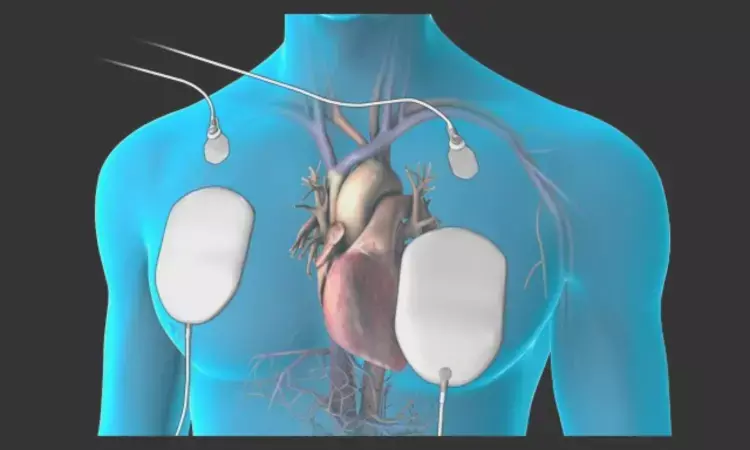
USA: The success rate of direct current (DC) cardioversion of atrial fibrillation (AF) patients is not affected by whether the position of the electrode is anterior-posterior (AP) or anterior-lateral (AL), a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) has shown.
The study results, published in the December 2022 issue of IJC Heart & Vasculature, imply that either AL or AP electrode positions should be acceptable for elective DC cardioversion of atrial fibrillation patients.
In clinical practice, atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. Direct current of AF is commonly indicated either on an elective basis in patients planned for rhythm control strategy or on an emergent basis for unstable patients. Hence, it becomes clinically essential to establish the safety and efficacy of cardioversion approaches.
Electrode and paddle positions, determining factors for the vector of DC cardioversion, have been proposed as critical in deciding procedure success. AP and AL electrode positions are the most common and most thoroughly studied. Several RCTs have evaluated the comparative efficacy of AP versus AL position during AF's cardioversion but have yielded mixed results.
Against the above background, Mennaallah Eid, Department of Internal Medicine, Lincoln Medical Center, New York, NY, United States, and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis and systematic review, including RCTs evaluating AP's efficacy versus AL electrode position in DC cardioversion of atrial fibrillation.
For this purpose, the researcher searched the online databases through March 2022 for randomized trials that assessed the outcomes of AP versus AL electrodes position during cardioversion. The study's primary outcome was the success rate of cardioversion (of atrial fibrillation).
The study led to the following findings:
- 10 RCTs were included in the final analysis, with 1677 patients.
- No difference was seen in the successful cardioversion rate between the AP compared to the AL groups (86.6 vs. 87.9 %; RR 1.00).
- No significant interaction between monophasic and biphasic waveforms was shown in the subgroup analysis by the shock waveform.
- Meta-regression analyses demonstrated no effect modification of primary outcome according to left atrial diameter, body mass index, valvular heart disease, lone AF, or the duration of AF.
- No significant difference was observed between the AP and AL electrode position groups in successful cardioversion at low energy (RR 0.94), the mean energy of the delivered shocks (standardizeS mean difference [SMD]−0.11), or the number of the delivered shocks (SMD −0.03).
- Lower transthoracic impedance was seen with AP versus AL electrode position (SMD −0.28).
The researchers found no difference between the electrode positions AP and AL in the success rate of AF's cardioversion. Also, no differences were seen in success rate at low shock energy, mean energy, or the number of shocks needed for cardioversion between the AL and AP electrode positions.
"Either AL or AP electrode positions should be acceptable strategies for elective DC cardioversion of atrial fibrillation patients," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Eid M, Abu Jazar D, Medhekar A, Khalife W, Javaid A, Ahsan C, Shabarek N, Saad M, Rao M, Ong K, Jneid H, Elbadawi A. Anterior-Posterior versus anterior-lateral electrodes position for electrical cardioversion of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022 Oct 21;43:101129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101129. PMID: 36304256; PMCID: PMC9593304.
Dr Kartikeya Kohli is an Internal Medicine Consultant at Sitaram Bhartia Hospital in Delhi with super speciality training in Nephrology. He has worked with various eminent hospitals like Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, Sir Gangaram Hospital. He holds an MBBS from Kasturba Medical College Manipal, DNB Internal Medicine, Post Graduate Diploma in Clinical Research and Business Development, Fellow DNB Nephrology, MRCP and ECFMG Certification. He has been closely associated with India Medical Association South Delhi Branch and Delhi Medical Association and has been organising continuing medical education programs on their behalf from time to time. Further he has been contributing medical articles for their newsletters as well. He is also associated with electronic media and TV for conduction and presentation of health programs. He has been associated with Medical Dialogues for last 3 years and contributing articles on regular basis.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


