- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Everolimus-eluting resorbable scaffold superior to angioplasty for CLTI due to infrapopliteal artery disease
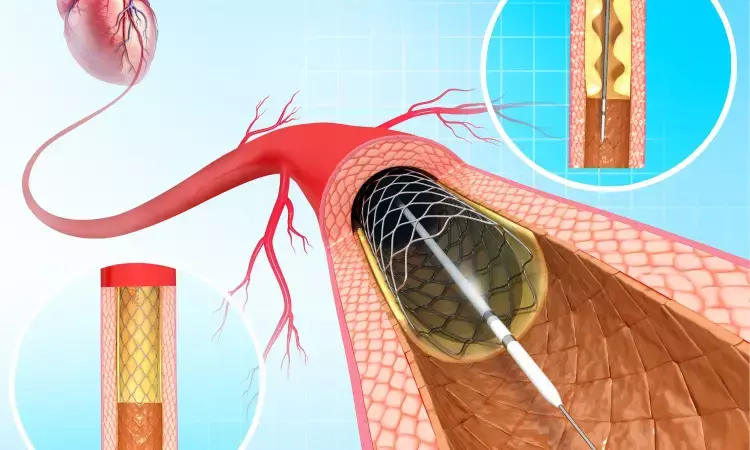
The results of the LIFE-BTK trial indicate that an everolimus-eluting resorbable scaffold is more effective than balloon angioplasty in reducing lower extremity limb events.
In terms of the primary efficacy endpoint, the use of an everolimus-eluting resorbable scaffold is more effective than angioplasty among patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI ) due to infrapopliteal artery disease, says Varcoe et al. and colleagues in there recent study published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Among patients with CLTI and infrapopliteal artery disease, angioplasty is tied to frequent reintervention and adverse limb outcomes from restenosis. There needs to be more data available regarding the effect of the use of drug-eluting resorbable scaffolds on these outcomes. This was further investigated in the present study.
This multi-centre, randomized, controlled trial had 261 patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) and infrapopliteal artery disease (2:1 ratio). The patients received either an everolimus-eluting resorbable scaffold or an angioplasty.
Freedom from amputation above the ankle, occlusion of the target vessel, clinically driven revascularization of the target lesion, and binary restenosis of the target lesion at 1 year was the primary efficacy endpoint.
The primary safety endpoint was freedom from major adverse limb events at six months and perioperative death.
Key results from the study are:
- No events occurred (primary efficacy end point) in 135/173 patients in the scaffold group and 48/88 patients in the angioplasty group.
- Kaplan–Meier estimate was 74% vs 44%, and the absolute difference was 30 percentage points.
- The primary safety endpoint was observed in 165 /170 patients (97%) and 90/90 patients (100%) in the scaffold and angioplasty groups, respectively. The absolute difference was −3 percentage points.
- Serious adverse events (index procedure-related) occurred in 2% of the patients in the scaffold group and 3% in the angioplasty group.
In conclusion, considering the primary efficacy endpoint, using an everolimus-eluting resorbable scaffold is superior to angioplasty in patients with CLTI due to infrapopliteal artery disease. It could be a novel strategy for reducing lower extremity limb outcomes.
Abbott funded the study.
Reference:
Ramon L. Varcoe. Drug-Eluting Resorbable Scaffold versus Angioplasty for Infrapopliteal Artery Disease.October 25, 2023. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2305637
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


