- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
HGF Plasmid Therapy Accelerates Healing in Limb-Threatening Ischemia,reveals study
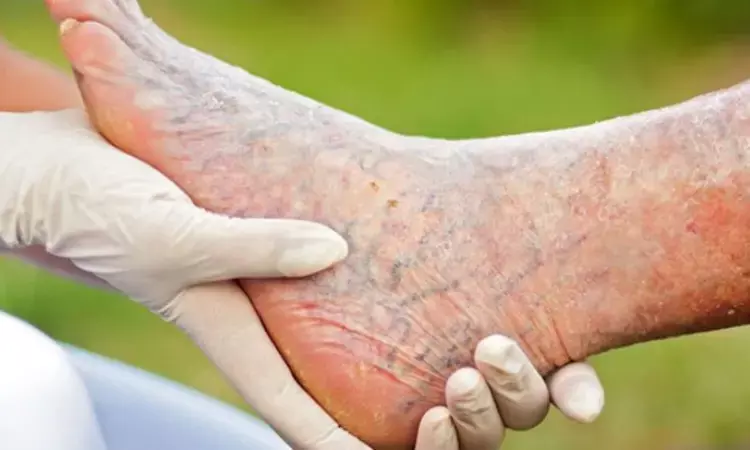
A new clinical trial demonstrates that hepatocyte growth factor plasmid therapy with AMG0001 is a promising, nonsurgical treatment option for accelerating wound healing in patients with moderate chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI). Patients with CLTI have no FDA-approved pharmacologic therapy specifically targeting ulcer healing; therefore, there is a large therapeutic need. The study was published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions by David G. and colleagues.
LEGenD-1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial conducted at 22 sites in the United States. A total of 75 subjects with neuroischemic ulcers and moderate CLTI were enrolled. Eligibility required toe pressure or TcPO₂ between 30 and 59 mm Hg. Participants were randomized to AMG0001 4 mg, AMG0001 8 mg, or placebo in a 1:1:1 ratio, and received intramuscular injections along a target arterial path at days 0, 28, 56, and 84, guided by angiography. Co-primary endpoints were:
Time to complete ulcer healing
• Proportion of subjects with ulcers healed at 6 months (pooled AMG0001 analysis).
• Secondary endpoints included healing at 12 months, ulcer recurrence, and hemodynamic measures.
Results
• Baseline characteristics were comparable between the treatment groups: participants had a mean age of 62.6 years, 80.0% were male, and 70.7% had diabetes.
• The mean toe pressure was 46.1 mmHg, whereas TcPO₂ averaged 49.8 mmHg, reflecting moderate ischemia.
• AMG0001 significantly reduced healing time.
The median time to complete healing was:
• 84 days for pooled AMG0001 versus 280 days for placebo (P = 0.007)
• 98 days for the 4 mg dose (P = 0.017)
• 84 days for the 8 mg dose (P = 0.022)
At 6 months, the healing occurred in:
• 63.3% of participants in the AMG0001 group vs 38.5% with placebo (P = 0.053)
At 12 months, healing rates increased to:
• 77.6% vs 46.2%, respectively, for AMG0001 and placebo; P = 0.010
• Adverse events were similar across groups, showing an acceptable safety profile.
Anatomically targeted intramuscular administration of the HGF plasmid AMG0001 significantly accelerated healing and improved long-term ulcer outcomes in patients with moderate CLTI and neuroischemic ulcers. In the absence of FDA-approved therapies for ulcer healing in this population, these results establish AMG0001 as a promising nonsurgical therapeutic option. Larger controlled trials will be required to confirm long-term safety, establish efficacy, and justify further development toward regulatory approval.
Reference:
Armstrong DG, Conte MS, Mills JL, Menard MT, Orgill DP, Galiano RD, Kirsner RS, Farber A, Lantis JC, Zelen CM, Carter MJ, Hicks CW, Powell RJ. Anatomically Directed Lower Extremity Gene Therapy for Ulcer Healing: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study (LEGenD-1). Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2025 Nov 4:e015648. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.125.015648. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 41186002.
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


