- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Isolated systolic hypertension strongly linked to traditional Obesity Indicators
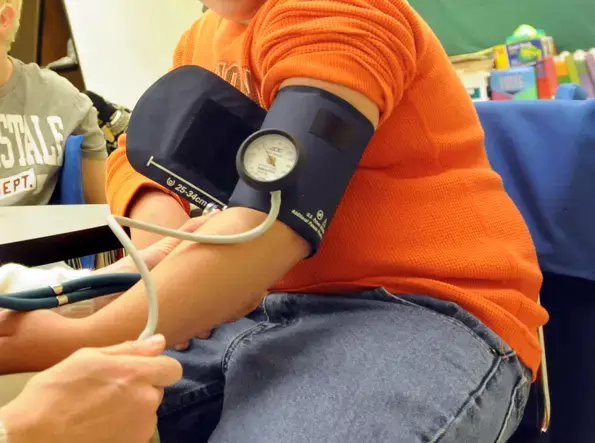
Numerous studies have demonstrated that isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) has an important role in predicting cardiovascular risk and all-cause mortality in both young and elderly adults. Obesity is also a well-established and modifiable risk factor for hypertension.
A recent study suggests that the association of traditional obesity indicators with isolated systolic hypertension was more prominent than that of lipid-related obesity indicators. The study findings were published in the BMC Cardiovascular Disorders on March 21, 2022.
Although several studies have demonstrated that these novel lipid-related obesity indicators were positively associated with hypertension, there are no data on their association with ISH and whether they have an advantage over traditional indicators. Therefore, Dr Xing Zhen Liu and his team conducted a study and compared the association of body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-height ratio (WHtR), visceral adiposity index (VAI), lipid accumulation product index (LAP), and cardiometabolic index (CMI) with ISH.
In a cross-sectional study, the researchers included 106,248 adults who received routine health screening and did not have diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg. They evaluated the associations between these indicators and ISH using multivariate regression. They obtained SBP, DBP, and heart rate (HR) 3 times on the right arm after at least 5 min of rest using an automatic BP monitor (HEM-1000, OMRON, Japan).
Key findings of the study:
- Upon analysis, the researchers found that each standard deviation (SD) increase in traditional obesity indicators (especially WHR and WHtR) had significantly higher multivariate-adjusted odds ratios (ORs) than each SD increase in lipid-related obesity indicators.
- They further found that the multivariate-adjusted ORs for ISH in the third (vs the first) tertile of traditional obesity indicators were also significantly higher than those of lipid-related indicators.
- They noted that the traditional obesity indicators exhibited a higher area under the ROC curve for discriminating ISH than lipid-related obesity indicators.
The authors concluded, "Compared with lipid-related obesity indicators, traditional ones such as BMI, WC, WHR, and WHtR were more associated with isolated systolic hypertension among Chinese adults. Therefore, these simple and economical anthropometric indicators can still play a role in the weight monitoring among ISH individuals."
For further information:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-022-02564-2
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


