- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ivabradine may revolutionize rate control in Rheumatic Atrial Fibrillation

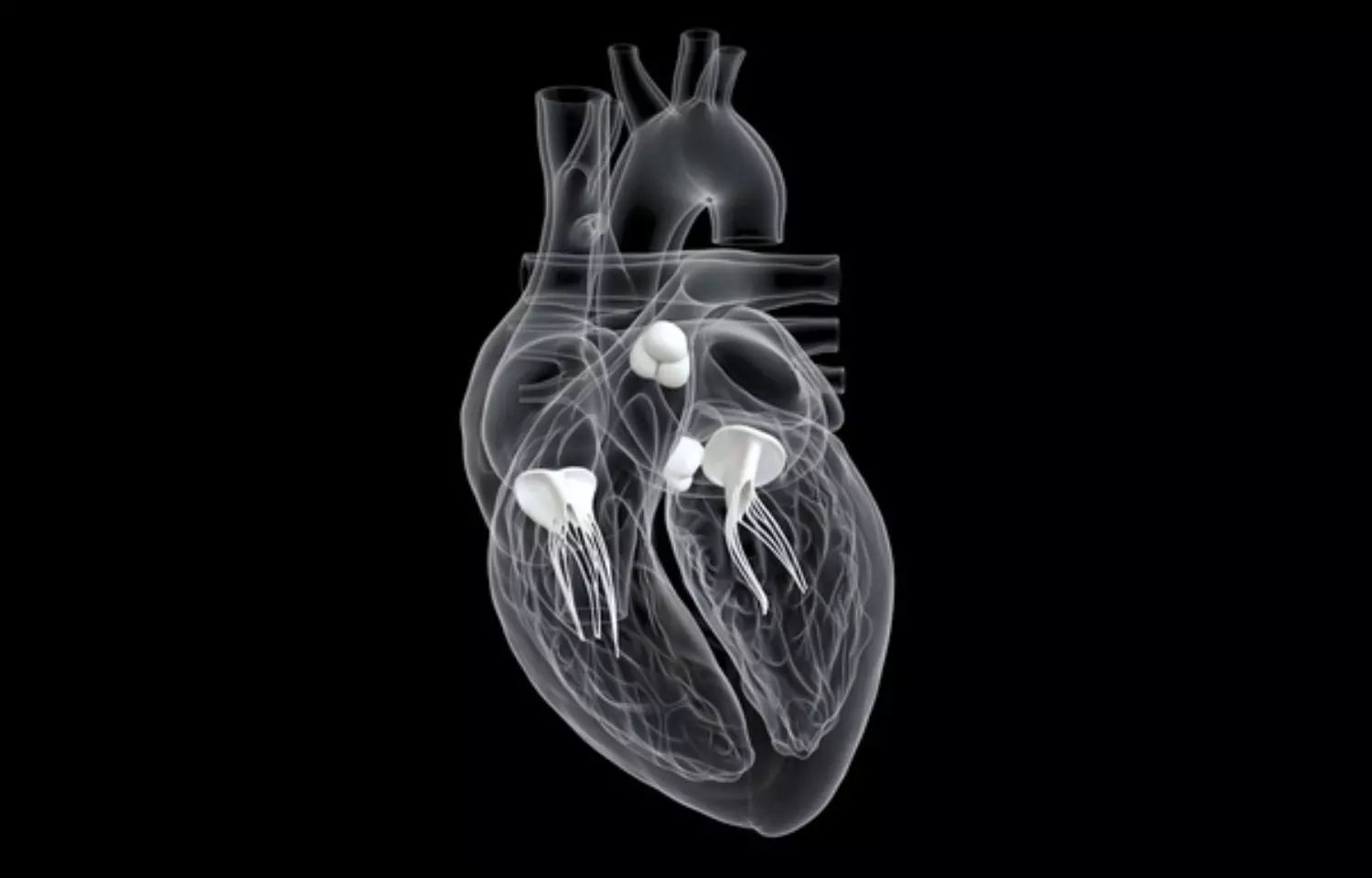
A potential game-changer in the management of Rheumatic atrial fibrillation (AF) has emerged, with Ivabradine taking the spotlight as a promising agent for controlling heart rates in patients suffering from this cardiac condition. The breakthrough comes as a result of Ivabradine's influence on HCN channels within the atrioventricular (AV) node.
The study results were published in the Indian Heart Journal on September 2, 2023.
Rheumatic heart disease is the common cause of Atrial fibrillation and it is a significant concern in cardiovascular medicine. Rate control is a crucial aspect of managing AF and it is a default treatment strategy. Ivabradine is a novel heart rate-reducing agent, now demonstrating remarkable potential in this area.
Researchers from the Department of Cardiology, Sanjay Gandhi PGIMS, Lucknow, 226014, India conducted a prospective single-center, randomized study to assess the safety and efficacy of Ivabradine as add-on therapy for rate control in patients with persistent and/or permanent rheumatic AF and already on maximally tolerated doses of either ββ or CCB.
About 80 patients diagnosed with rheumatic AF, having a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute, showed promising results. Patients were randomized to either continue their existing medication regimen, typically beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, or switch to Ivabradine. Ivabradine was introduced at a dose of 2.5 mg twice daily increased to 5 mg BD if inadequate response at 1 week. Dose escalation to 7.5mg BD was done after Holter at 1 month.
The results were striking.
- Significant reduction in heart rates compared to the control group was observed at 3 and 6 months.
- The absolute reduction in heart rate and percentage change were both notably higher in the Ivabradine group.
- Additionally, at the 6-month mark, the Ivabradine-treated patients experienced lower NT Pro BNP levels, improved exercise tolerance, better symptom relief, and enhanced left atrial strain, all of which indicated improved cardiac function and overall well-being.
- Crucially, Ivabradine was well-tolerated, with no reported cases of drug withdrawal.
This suggests that Ivabradine may be a viable option for rate control in rheumatic AF, potentially offering a more effective and patient-friendly alternative to current therapies. Ivabradine could herald a new era in the management of atrial fibrillation, offering hope for improved quality of life and better cardiac health for millions of individuals affected by this condition.
Further reading: A pilot study evaluating the role of ivabradine for rate control in patients with rheumatic atrial fibrillation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2023.08.006
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751