- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Manual compression hemostasis with novel hemostatic pad revolutionizes distal radial artery approach for diagnostic catheterization: Study
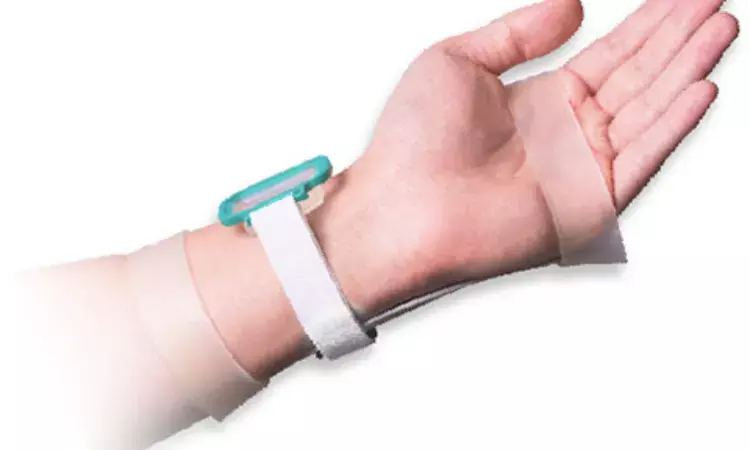
Japan: A pioneering technique in interventional cardiology, manual compression hemostasis using a hemostatic pad for the distal radial artery approach, is poised to revolutionize vascular access procedures. This groundbreaking method promises improved patient comfort, enhanced procedural efficiency, and reduced complication rates, significantly advancing cardiac catheterization procedures.
The study, published in Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine, revealed the feasibility of manual compression hemostasis using calcium alginate pads for the distal radial artery approach with simple learning.
Traditionally, achieving hemostasis following radial artery access has relied on prolonged manual compression or the application of mechanical compression devices. While effective, these methods often entail prolonged immobilization, discomfort, and potential complications such as radial artery occlusion. The advent of the hemostatic pad offers a promising alternative, streamlining the hemostasis process and optimizing patient outcomes.
The hemostatic pad, composed of a unique blend of absorbent materials and hemostatic agents, is designed to accelerate the hemostasis process while ensuring optimal patient comfort. Upon completion of the catheterization procedure, the pad is applied directly over the puncture site, exerting controlled pressure to facilitate rapid sealing of the arterial puncture site.
The method of hemostasis for the distal radial approach has not been standardized, although this approach has gained immense popularity due to its advantages. In this study, Kenji Sadamatsu, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Omuta City Hospital, Omuta, Japan, and colleagues investigated the feasibility of manual compression hemostasis using a calcium alginate pad after coronary angiography via the distal radial approach.
For this purpose, the researchers retrospectively collected 150 consecutive patients (mean age, 74.9 ± 8.0 years; male, 75 %) who underwent coronary angiography via the distal radial artery with a predominantly 4 Fr sheath from 2021 to 2022 and were hemostatic according to the following methods.
After sheath removal, hemostasis was achieved by manual compression for 10 min using a hemostatic pad containing calcium alginate. After hemostasis confirmation, a small log-shaped gauze was placed over the pad and fixed using a self-adhesive elastic bandage for two hours. All procedures were conducted by four fellows just beginning the distal radial approach.
The study led to the following findings:
- The mean compression time was 12.4 ± 4.8 min, and hemostasis was successfully achieved in all patients, allowing the release of the elastic bandage after 2 h, with only one patient oozing the next morning.
- There were no major complications, while one patient had a >10 cm hematoma.
- Compared to that of the first 15 patients, for each fellow, the compression time of the subsequent patients was significantly shorter (14.5 ± 6.7 versus 11.1 ± 2.1 min).
"Our observational study revealed that manual compression hemostasis using a calcium alginate pad was effective and feasible for dRA in a senior population undergoing diagnostic catheterization with predominantly a 4F sheath with 3000 units of heparin," the researchers wrote. "With this method, even trainees could achieve hemostasis, and the hemostasis time was stable after the first 15 patients."
Reference:
Sadamatsu, K., Kugai, T., Eto, Y., Muta, M., Maeda, T., Ishimatsu, T., Shihara, M., & Fukumoto, Y. (2024). Manual compression hemostasis using a hemostatic pad for the distal radial artery approach. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carrev.2024.05.028
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


