- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Meta-analysis details different obstructive sleep apnea treatments for lowering BP
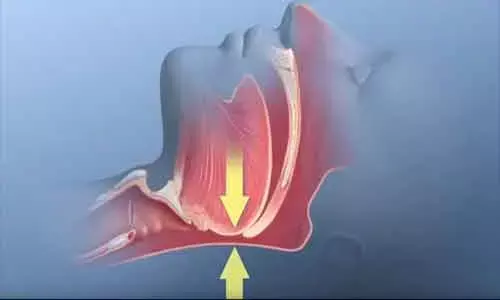
China: In patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) can effectively reduce blood pressure (BP), a research shows. Renal sympathetic denervation (RDN) is a novel hypertension treatment that lowered BP in such patients.
"CPAP might be helpful as adjunctive therapy in OSA patients with hypertension as it was associated with mild but stable BP reduction," Jing Yu, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Hypertension Centre, Lanzhou, Gansu, China, and colleagues wrote in their study published in the Journal of Hypertension.
Obstructive sleep apnoea is a common cause of secondary hypertension. The researchers aimed to assess the effect of different OSA treatments on lowering blood pressure in a network meta-analysis (NMA).
For this purpose, the researchers searched the online databases for relevant randomized controlled trials. The search strategies included the concepts of OSA, hypertension, blood pressure, and blood pressure-reducing treatments without language or data restriction (from inception to 1 June 2021).
The outcomes included office DBP, office SBP, daytime SBP (dSBP) and DBP (dDBP), and DBP (nDBP) and night-time SBP (nSBP). The researchers performed a Bayesian network meta-analysis.
Salient findings of the study include:
- The researchers reviewed 49 randomized controlled trials involving 4893 patients and the following interventions: mandibular advancement devices, : continuous positive-airway pressure (CPAP), nocturnal supplemental oxygen, surgery, β-blocker, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), renal sympathetic denervation (RDN), calcium channel blockers.
- MRAs were significantly associated with blood pressure reduction followed by ACEI/ARB. RDN could reduce office SBP, office DBP, 24-h SBP, 24-h DBP, dSBP, and dDBP.
- CPAP also demonstrated modest blood pressure lowering.
"MRAs and ACEIs/ARBs can effectively reduce BP effectively in OSA patients. RDN is a novel hypertension treatment that lowered BP in such patients," the authors wrote in their study.
"CPAP was associated with mild but stable blood pressure reduction, and it might be helpful as an adjunctive therapy in OSA patients with hypertension."
Reference:
Kou, Chengkun∗; Zhao, Xu∗; Lin, Xin; Fan, Xin; Wang, Qiongying; Yu, Jing Effect of different treatments for obstructive sleep apnoea on blood pressure, Journal of Hypertension: June 2022 - Volume 40 - Issue 6 - p 1071-1084 doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003131
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


