- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sleep restriction tied to persistent rise in BP in healthy young adults: Study
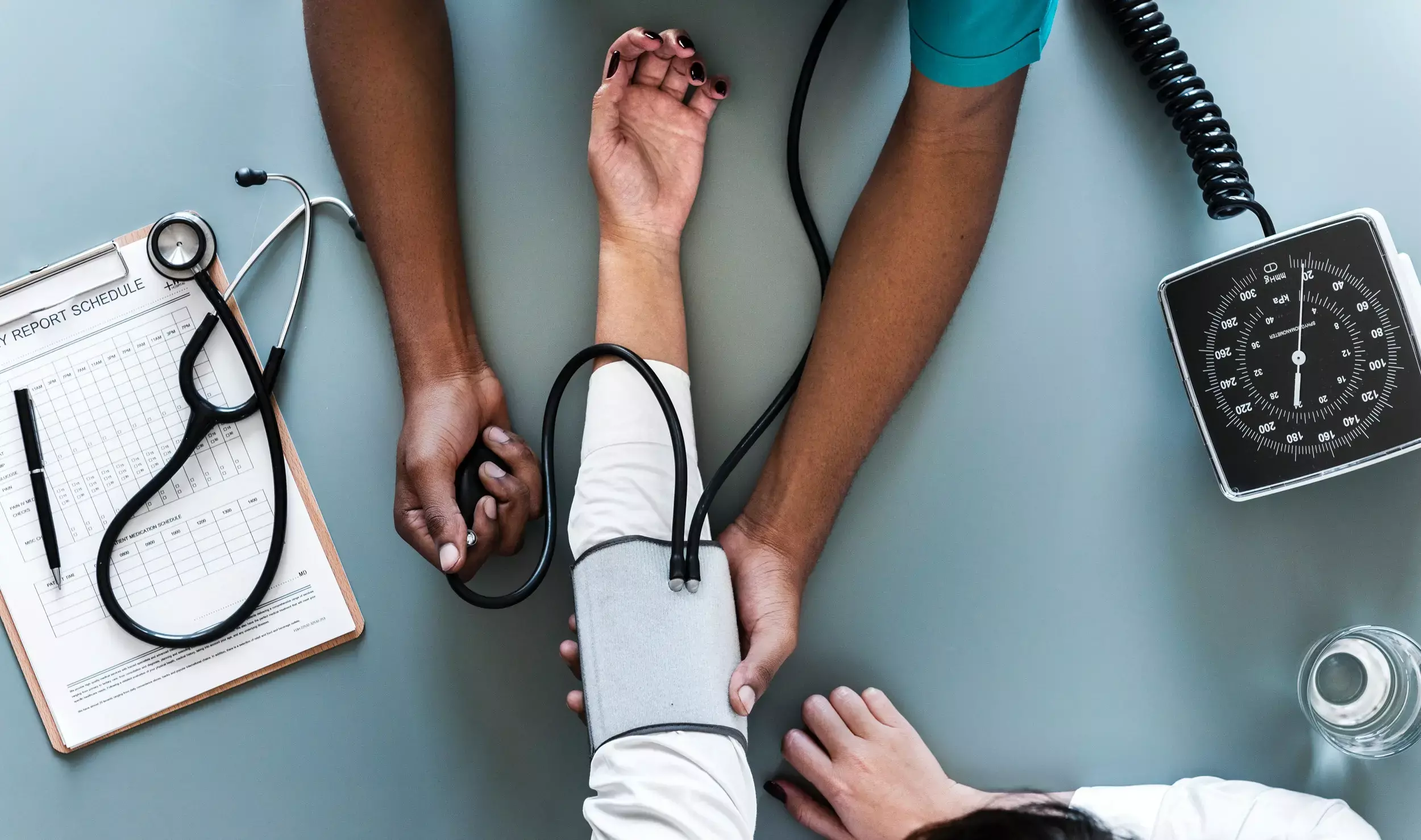
Although insufficient sleep is associated with increased cardiovascular risk, evidence of a causal relationship is lacking. As per a recent research published in Hypertension, researchers have observed that shortened sleep causes persistent elevation in 24-hour and sleep-time BP.
Naima Covassin and team from the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN investigated the effects of prolonged sleep restriction on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure (BP) and other cardiovascular measures in 20 healthy young participants aged 23.4±4.8 years, out of which 9 were females, all of whom underwent a randomized, controlled, crossover, 16-day inpatient study consisting of 4 days of acclimation, 9 days of sleep restriction (4 hours of sleep/night) or control sleep (9 hours), and 3 days of recovery.
These subjects consumed a weight maintenance diet with controlled nutrient composition throughout. A 24-hour BP (primary outcome) and cardiovascular biomarkers were measured repeatedly. Polysomnographic monitoring was continuous.
Comparing sleep restriction versus control sleep, it was observed that 24-hour mean BP was higher (adjusted mean difference, day 12: 2.1 mm Hg [95% CI, 0.6–3.6], corrected P=0.016), endothelial function was attenuated (P<0.001), and plasma norepinephrine increased (P=0.011).
Despite increased deep sleep, BP was elevated while asleep during sleep restriction and recovery. Post hoc analysis revealed that 24-hour BP, wakefulness, and sleep BP increased during experimental and recovery phases of sleep restriction only in women, in whom 24-hour and sleep systolic BP increased by 8.0 (5.1–10.8) and 11.3 (5.9–16.7) mm Hg, respectively (both P<0.001).
Therefore, it was concluded that shortened sleep causes persistent elevation in 24-hour and sleep-time BP. Pressor effects are evident despite closely controlled food intake and weight, suggesting that they are primarily driven by the shortened sleep duration.
BP increases are especially striking and sustained in women, possibly suggesting lack of adaptation to sleep loss and thus greater vulnerability to its adverse cardiovascular effects, they further inferred.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


