- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Low-normal oxygenation targets may not reduce organ dysfunction in critically ill: JAMA
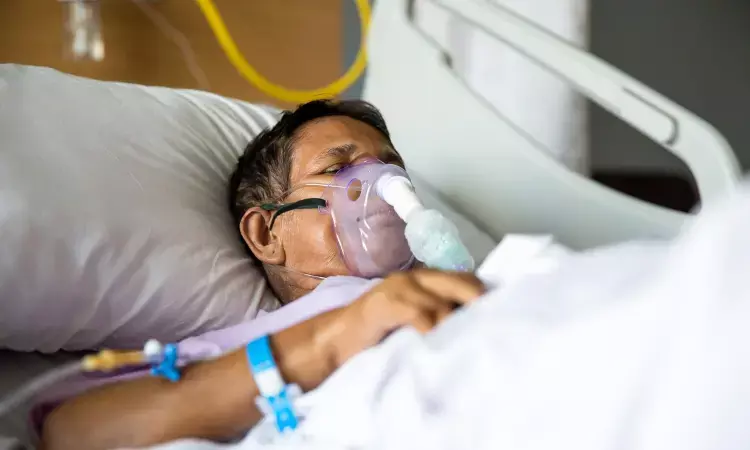
Targeting oxygenation to a low-normal range compared with a high-normal range does not result in a statistically significant reduction in organ dysfunction in critically ill patients suggests a study published in the JAMA.
Hyperoxemia may increase organ dysfunction in critically ill patients, but optimal oxygenation targets are unknown.
A study was conducted by a group of researchers from the Netherlands to determine whether a low-normal Pao2 target compared with a high-normal target reduces organ dysfunction in critically ill patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
It was a multi-centre randomized clinical trial in 4 intensive care units in the Netherlands. Enrollment was from February 2015 to October 2018, with the end of the follow-up to January 2019, and included adult patients admitted with 2 or more SIRS criteria and expected a stay of longer than 48 hours. A total of 9925 patients were screened for eligibility, of whom 574 fulfilled the enrollment criteria and were randomized.
The primary endpoint was SOFARANK, a ranked outcome of non-respiratory organ failure quantified by the non-respiratory components of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score, summed over the first 14 study days. Participants were ranked from fastest organ failure improvement (lowest scores) to worsening organ failure or death (highest scores). Secondary endpoints were duration of mechanical ventilation, in-hospital mortality, and hypoxemic measurements.
The results of the study are as follows:
- Among the 574 patients were randomized, 400 (70%) were enrolled within 24 hours, all of whom completed the trial.
- The median Pao2 difference between the groups was −1.93 kPa.
- The median SOFARANK score was −35 points in the low-normal Pao2 group vs −40 in the high-normal Pao2 group.
- There was no significant difference in the median duration of mechanical ventilation.
- Mild hypoxemic measurements occurred more often in the low-normal group.
- Acute kidney failure developed in 20 patients (10%) in the low-normal Pao2 group and 21 patients (11%) in the high-normal Pao2 group, and acute myocardial infarction in 6 patients (2.9%) in the low-normal Pao2 group and 7 patients (3.6%) in the high-normal Pao2 group.
Thus, the researchers concluded that among critically ill patients with 2 or more SIRS criteria, treatment with a low-normal Pao2 target compared with a high-normal Pao2 target did not result in a statistically significant reduction in organ dysfunction. However, the study may have had limited power to detect a smaller treatment effect than was hypothesized.
Reference:
Effect of Low-Normal vs High-Normal Oxygenation Targets on Organ Dysfunction in Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial by Gelissen H et. al published in the JAMA
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.13011
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


