- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dental Caries- Standard Treatment Guidelines
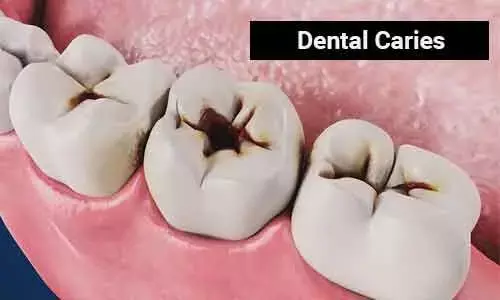
Dental caries is an infectious microbiologic disease of the calcified tissues of the teeth, characterized by demineralization of the inorganic portion and destruction of the organic substance of the tooth. It is a common chronic disease that leads to pain and disability across all age groups. The infection results in loss of tooth minerals that begin on the outer surface of the tooth and can progress through the dentin to the pulp, ultimately compromising the vitality of the tooth. If left untreated, it may lead to pain, infection and even tooth loss. During the past few decades, changes have been observed not only in the prevalence of dental caries but also in the distribution and pattern of the disease in the population.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has released standard treatment guidelines for treatment of Dental caries. Following are its major recommnedations
INCIDENCE OF THE CONDITION IN OUR COUNTRY
In the 1940s the prevalence of dental caries in India was 55.5% while in the 1960's it was reported to be 68%. Recent studies show an incidence ranging from 44 - 73%.ln order to make continued progress in eliminating this common disease, new strategies will be required :
• To provide enhanced access for those who suffer disproportionately from the disease.
• To provide improved detection, risk assessment, and diagnosis.
• To create improved methods to arrest or reverse the noncavitated lesion while improving surgical management of the cavitated lesion.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Essentially any condition having the onset of sensitivity or acute pain. Important ones include:
• Hypersensitivity
• Abrasions
• Periapical abscess
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA, INVESTIGATIONS, TREATMENT & REFERRAL CRITERIA
LEVEL 1: AT SOLO PHYSICIAN CLINIC :
Clinical Diagnosis:
• Visual inspection of the oral cavity.
• To check for black spots on the teeth which are supposed to be paining.
• Patients complain of increased sensitivity to hot and cold.
• Pain on percussion of the effected tooth/teeth.
• Swelling in relation to the effected tooth.
• Restricted mouth opening.
• Tenderness of draining lymph nodes.
Treatment:
• If only sensitive to hot and cold then refer to Dental surgeon at level four
• In case of acute pain and swelling start antibiotics and analgesics
• Cap Amoxicillin 30-40 mg/kg /day 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Tab Paracetamol 500mg 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Tab Brufen 400mg 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Antiplaque mouth wash containing Triclosan ( 5 ml ) twice a day.
• Inform the patient to do warm saline gargles 8-12 times daily in case of swelling.
Referral criteria:
• Increased sensitivity to hot and cold for more than two weeks
• Mouth opening restricted and pain not subsiding for more than a week
• Infra oral sinus
• Extraoral sinus
• Refer cases to level 4 as Dental surgeons are available there
LEVEL 2: AT 6-10 BEDDED PRIMARY HEALTH CENTRE
Clinical Diagnosis: Same as Level 1 fora fresh case reporting directly
Treatment: Same as Level 1
Referral criteria: Same as Level 1
LEVEL 3: AT 30-100 BEDDED COMMUNITY HEALTH CENTRE
Clinical Diagnosis: Same as level 1
Investigations:
• Intraoral radiograph to check for pulpal involvement
• If an extraoral sinus exists then pus culture and sensitivity can be done and medications are given accordingly.
Treatment: Same as Level 1 except that the medication will be according to culture and sensitivity test.
Referral criteria: Same as level 1
LEVEL 4: AT 100 OR MORE BEDDED DISTRICT HOSPITAL
Clinical Diagnosis
• Visual inspection of the oral cavity
• Check for black spots on the teeth which are supposed to be paining
• Patients complain of increased sensitivity to hot and cold
• Pain on percussion of the effected tooth /teeth
• Swelling in relation to the effected tooth /teeth
• Restricted mouth opening
• Draining lymph nodes tender
Investigations:
• Intraoral periapical radiographs to check whether a pulp is involved or not
• Vitality test of the tooth
Treatment:
• If caries not involving the pulp restoration is suggested
• In the case of abscess drain the abscess and open the root canals.
• Pulpotomy/ pulpectomy
• In the case where the pulp is involved - Root Canal Treatment
• Extraction of the tooth if the tooth is highly decayed
• Institute medication in case of swelling/cellulitis or abscess
• CapAmoxicillin 30-40 mg/kg /day 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Tab Tinidazole 500 mg - 12hourly for 5 days.
• Tab Paracetamol 500mg - 8 hourly for 5 days.
• Tab Brufen 400mg - 8 hourly for 5 days.
Follow up:
• Recall the patient after a week to check the restorations.
• In the case of Root Canal Treatment recall the patients after 2 weeks to check the status and to examine any signs of swelling/ intraoral sinus.
• Permanent restoration of Root Canal Treated tooth with a crown ( Metal/ Porcelain) after six weeks.
• Check the level of oral hygiene measures instituted by the individual.
• Recall of the patient every six months to examine the development of new carious lesions.
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


