- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI may help design dental crowns based on a valid 3D deep learning algorithm
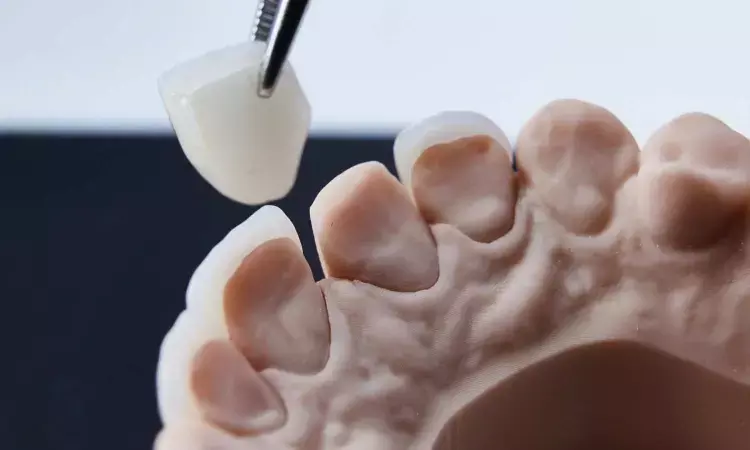
Hong Kong: Researchers at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) have developed 3D-DCGAN that may help design dental crowns based on a valid 3D deep learning algorithm. Further 3D-DCGAN could be used to design personalised dental crowns with high accuracy that can mimic both the biomechanics and morphology of natural teeth.
The results of research have been published in the leading academic journal Dental Materials.
The researchers developed a generative AI algorithm that uses a true three-dimensional (3D) deep learning approach, producing personalised dental crowns with high accuracy that mimic the morphology and match the materials required for the biomechanics of natural teeth. Biomechanical finite element analysis revealed that by using lithium silicate, the AI-designed crown can come very close to achieving the expected lifespan of natural teeth. In contrast, the two existing methods of designing dental crowns result in crowns that are either too large or too thin, and fall short of matching the same lifespan as natural teeth.
The team, led by Dr James Tsoi, Associate Professor in Dental Materials Science, collaborated with HKU Faculty of Engineering’s Department of Computer Science colleagues to leap forward for the next-generation AI-designed dental prosthesis production workflow.
Currently, the Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) digital workflow has significantly improved dentistry but still has its challenges. From the design to the manufacture of dental prostheses, the process is labour-intensive, time-consuming, and generates health and environmental hazards during the 3D printing and milling processes. The software uses a ‘tooth library’ that contains predefined crown templates to assist in generating prosthetic designs but further adjustments are still needed by the operator to meet individual conditions.
The smart manufacturing method developed by the research team can meet the challenge and help replace the conventional approach to designing personalised dental crowns.
“We used a 3D-DCGAN (3D-Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network) approach to ‘teach’ the AI algorithm ‘good’ designs by feeding the algorithm with over 600 cases of natural and healthy dentition. The algorithm improves the quality of the design through internal competition between a generator and a discriminator,” said Dr Hao Ding, a co-investigator on the project.
“During the training process, natural teeth morphological features were learned by the algorithm, so that it can design dental crowns comparable to a natural tooth-both morphologically and functionally.” Dr Ding added.
The 3D-DCGAN AI-designed crowns were compared with natural teeth and with two other conventional CAD methods of crown design methods. The results revealed that the generative AI-designed crowns had the lowest 3D discrepancy, closest cusp angle (morphological feature), and similar occlusal contacts (functional feature) as compared to natural teeth.
“This demonstrates that 3D-DCGAN could be utilised to design personalised dental crowns with high accuracy that can not only mimic both the morphology and biomechanics of natural teeth but also operate without any additional human fine-tuning, thus saving additional costs in the production process,” said principal investigator Dr James Tsoi.
“Many AI approaches design a ‘look alike’ product, but I believe this is the first project that functionalises data-driven AI into the real dental application. We hope this smart manufacturing technology will be the stepping-stone for driving Industry 4.0 in dentistry, which is vital to meet the challenges of ageing society and lack of dental personnel in Hong Kong.” He added.
Dr Tsoi said the breakthrough marks an important step towards leveraging the dental industry in Great Bay Area, which sees an annual USD3.3B revenue for producing 25-30% dental prosthesis globally, and to align with the National 14th Five-year plan in developing new forms of industrialisation and informatisation viz. smart intelligent manufacturing.
Clinical trials for using this generative AI for dental crowns are underway. The team is also working on the applicability of this tool in other dental prostheses such as bridges and dentures.
Reference:
Hao Ding, Zhiming Cui, Ebrahim Maghami, Yanning Chen, Jukka Pekka Matinlinna, Edmond Ho Nang Pow, Alex Siu Lun Fok, Michael Francis Burrow, Wenping Wang, James Kit Hon Tsoi, Morphology and mechanical performance of dental crown designed by 3D-DCGAN, Dental Materials, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2023.02.001
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


