- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Are Robotic-Assisted Dental Implants more Accurate Than Freehand Surgery?
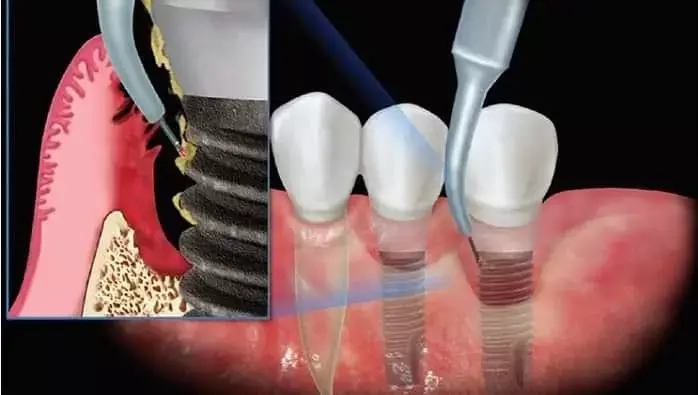
A recent clinical study revealed that robotic-assisted dental implant surgery offers significantly higher accuracy in implant placement when compared to traditional freehand techniques. However, the advanced robotic method requires a slightly longer operation time. The research was published in the Clinical Oral Implants Research journal followed patients for 6 months post-surgery and found no differences in safety or implant survival rates between the two techniques.
The study included a total of 24 patients, with a median age of 36, and 18 of them were female. The patients requiring single-tooth implant restorations were randomly assigned to either robotic-assisted or freehand surgery. Jiaxian Chen and team evaluated implant accuracy by comparing preoperative planning software data with immediate postoperative CBCT scans. They also recorded intraoperative and postoperative complications while documenting the time taken for implant placement.
The results of this study demonstrated a clear advantage in precision for robotic-assisted implants. Measurements of implant positioning deviations showed that the robotic-assisted method had an average platform global deviation of 0.70 mm, when compared to 1.24 mm in the freehand group. The apex global deviation was 0.70 mm for robotic-assisted surgery but significantly higher at 2.13 mm for freehand placement. Similarly, the angular deviation was much lower in the robotic group at 1.09°, whereas freehand placement had a deviation of 7.43°—a notable difference affecting the alignment of the implant.
Despite its higher accuracy, robotic-assisted surgery required more time, averaging 18.8 minutes per procedure. However, the study found no difference in intraoperative and postoperative complication rates between these 2 groups, and both methods achieved a 100% implant survival rate at the six-month follow-up.
While the robotic-assisted approach offers a clear advantage in precision, the study suggest that improvements in robot system design and registration could help streamline the process, making it more efficient and accessible for widespread clinical use. Overall, these findings highlight the growing role of robotics in dental surgery by emphasizing their potential to enhance precision and improve patient outcomes.
Reference:
Chen, J., Wang, Y., Bai, Y., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., Yan, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Accuracy, safety, and efficiency in robotic‐assisted vs. Freehand dental implant surgery: A 6‐month follow‐up randomized controlled trial. Clinical Oral Implants Research. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.14413
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


