- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Both Zirconia and Titanium Abutments show comparable Tissue Response and Volume Stability: Study
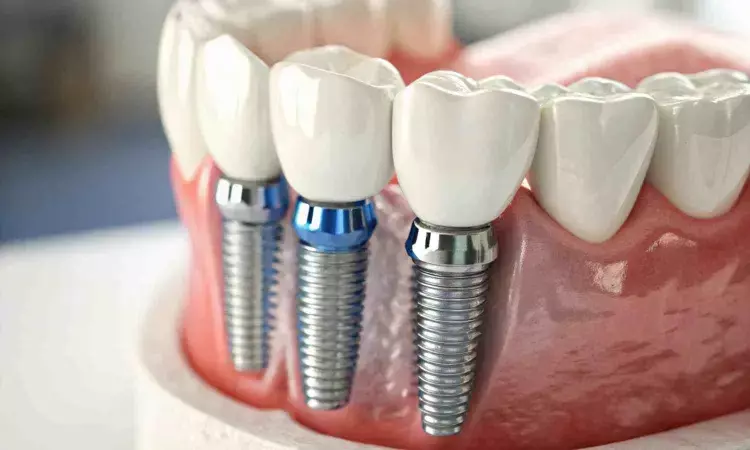
A new clinical study has found that zirconia (ZR) and customized titanium (CS) abutments yield comparable soft tissue responses and volume stability in dental implants. While both materials performed well, each showed unique advantages. ZR abutments were associated with shallower probing depths, suggesting a more favorable soft tissue condition.
In contrast, CS abutments demonstrated less volumetric shrinkage over time, indicating better maintenance of peri-implant contour.
The researchers assessed multiple indicators, including soft peri-implant tissue height (SPTH), probing depth (PD), and volumetric tissue changes. The SPTH remained stable in both groups, emphasizing that neither material compromised vertical tissue integrity over the 12-month follow-up period.
These findings contribute to the ongoing debate around the ideal abutment material for esthetic and functional outcomes in implant dentistry. Zirconia, often praised for its tooth-like color and biocompatibility, seems to promote better soft tissue health, especially in anterior regions. Titanium, especially when customized, offers better volume retention — a critical factor for long-term esthetics and tissue stability.
This research supports the idea that clinical decision-making can be more flexible, taking into account patient-specific needs such as esthetics, tissue thickness, and risk of inflammation. The authors suggest that both materials are reliable choices, and that their selection may come down to surgical protocol, prosthetic design, and patient anatomy.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


