- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Buccal sagittal root position and higher alveolar bone concavity angle may predict outcomes in immediate implant placement: Study
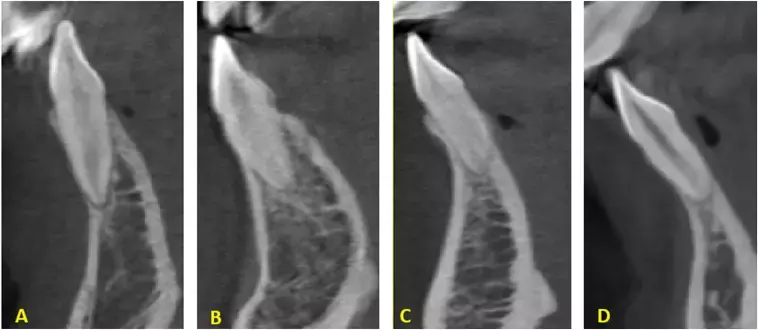
Buccal sagittal root position, higher alveolar bone concavity angle, and maxillary sinus proximity may predict outcomes in immediate implant placement suggests a study published in the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.
Immediate implant placement in the maxillary premolar area is challenged by anatomic variations imposing risks such as perforation of the buccal bone and the maxillary sinus. Previous studies have addressed the potentially relevant factors individually; a study assessing all relevant variables comprehensively and with a large sample size is lacking.
The purpose of this observational study was to analyze multiple anatomic considerations, including sagittal root position, alveolar bone concavity angle, buccal bone perforation, maxillary sinus floor root proximity, and maxillary sinus perforation in the maxillary premolar area, using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) to inform, perceive, and simplify the placement of immediate implants.
The analysis involved 333 CBCT images (189 of men, 144 of women). A total of 1332 first and second maxillary premolars were assessed for sagittal root position, alveolar bone concavity angle, buccal bone perforation, maxillary sinus floor root proximity, and maxillary sinus perforation. Chi-squared and kappa tests were used to analyze the distributions and agreement, respectively, while dependent and independent t tests were used to assess sex and tooth-specific differences.
The Spearman correlation test was used to explore the potential correlations (α=.05). Results: The majority of sagittal root position distribution was on the buccal side, ranging from 79.3% to 88.3%, while maxillary sinus floor root proximity showed a predominance of the T0 category (roots separated from the maxillary sinus floor), with noticeable sex disparities in the second right premolar (73% in men versus 50.7% in women; P<.001). The "perforation" category of buccal bone perforation was highest in the right first premolar (54.1%), being higher in women across all teeth.
The “perforation" category of maxillary sinus perforation was highest in the left second premolar (21.9%). Associations were found between buccal bone perforation and sagittal root position in the second premolars. The Spearman correlation between root proximity and sinus perforation was high, ranging from 0.68 to 0.78. The alveolar bone concavity angle in first premolars, compared with second premolars, poses a higher risk of buccal bone perforation, especially in women. The buccal position is the most common sagittal root position. The risk of sinus perforation is higher in maxillary second premolars, with proximity to or protrusion into the maxillary sinus floor categories strongly correlating with this complication. These findings highlight the importance of thorough assessment and strategic planning to ensure successful immediate implant placement and minimize potential complications.
Reference:
Alqutaibi AY, Aloufi AM, Hamadallah HH, Khaleefah FA, Tarawah RA, Almuzaini AS, Almashraqi A, Halboub E. Multifactorial analysis of the maxillary premolar area for immediate implant placement using cone beam computed tomography: A study of 333 maxillary images. J Prosthet Dent. 2024 Aug 1:S0022-3913(24)00468-2. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2024.07.010. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39095216.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


