- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
CAF, tunnelling procedures with CTG effective surgical option for Gingival recession: Study
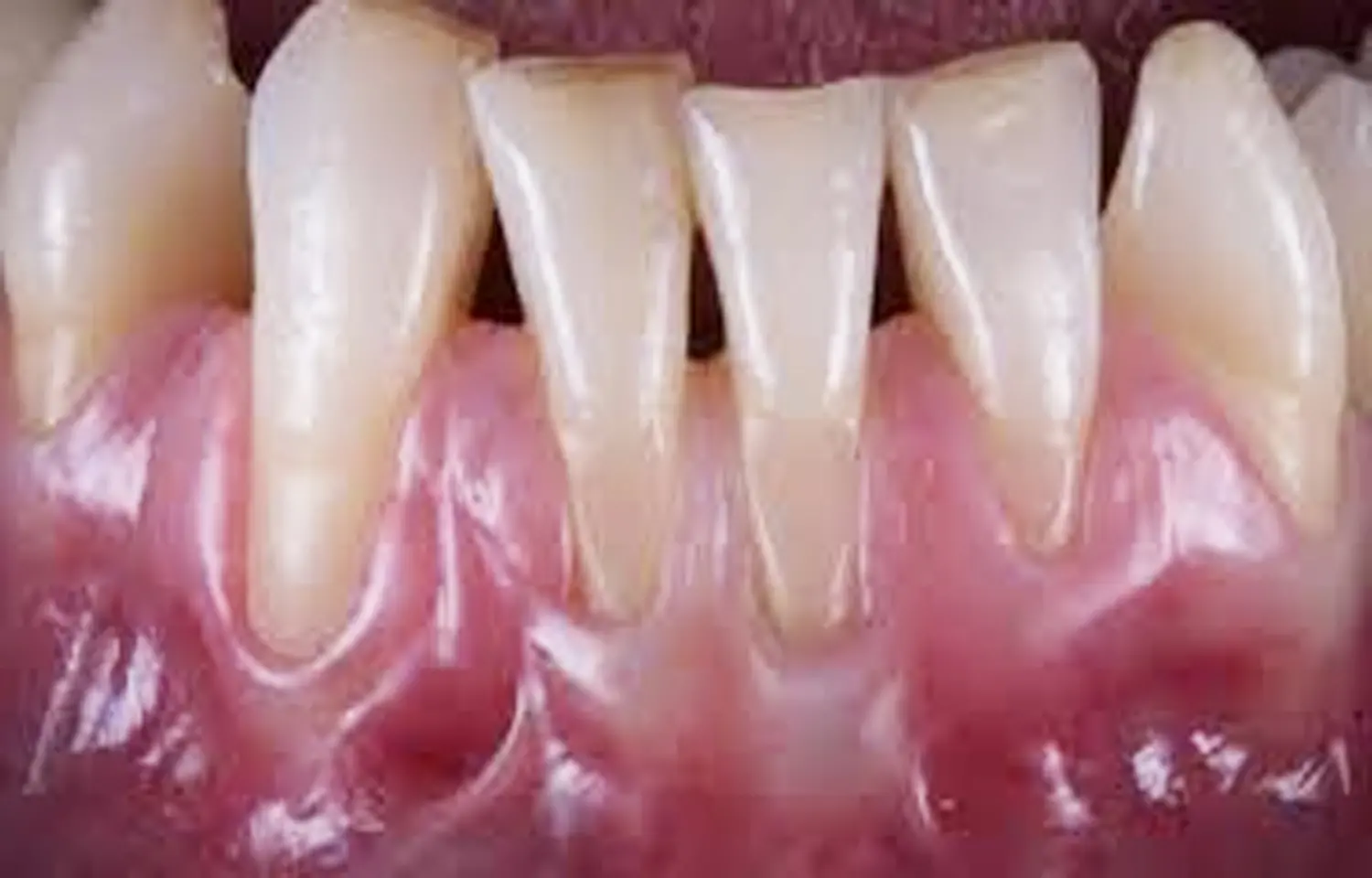
Gingival recession is a common finding in daily clinical practice. Several issues may be associated with the apical shift of the gingival margin such as dentine hypersensitivity, root caries, non-carious cervical lesions (NCCLs), and compromised aesthetics.
However, first step in an effective management and prevention program is to identify susceptibility factors and modifiable conditions associated with gingival recession, describes a recent study.
Researchers, Jean-Claude Imber and Adrian Kasaj from the Department of Periodontology and Operative Dentistry, University of Mainz, Mainz, Germany and Department of Periodontology, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland respectively carried out the present study to discuss the treatment options of gingival recession.
The study is published in the International Dental Journal.
According to the authors, when developing a treatment strategy, clinicians should first focus on susceptibility factors and modifiable conditions while increasing the patient's awareness about gingival recession.
Non-surgical treatment options for gingival recession defects include establishment of optimal plaque control, removal of overhanging subgingival restorations, behaviour change interventions, and use of desensitising agents.
In cases where a surgical approach is indicated, coronally advanced flap and tunnelling procedures combined with a connective tissue graft are considered the most predictable treatment options for single and multiple recession defects.
However, if there is a contraindication for harvesting a connective tissue graft from the palate or the patient wants to avoid a donor site surgery, adjunctive use of acellular dermal matrices, collagen matrices, and/or enamel matrix derivatives can be a valuable treatment alternative.
For gingival recession defects associated with NCCLs a combined restorative-surgical approach can provide favourable clinical outcomes.
Furthermore, if a patient refuses a surgical intervention or there are other contraindications for an invasive approach, gingival conditions should be maintained with preventive measures.
Therefore, the authors concluded that "in cases where a surgical approach is indicated, coronally advanced flap (CAF) and tunnelling procedures combined with a connective tissue graft (CTG) are considered the most predictable treatment options for single and multiple recession defects. If there is a contraindication for harvesting a CTG from the palate or the patient wants to avoid a donor site surgery, adjunctive use of ACDM, CM and/or EMD can be a valuable treatment alternative."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


