- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Can Working Length of ultrasonic tip impact Root Canal Dynamics?
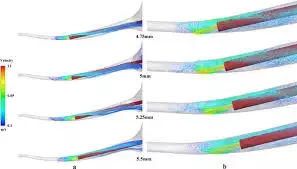
Researchers have found in a new study that increasing the working length of ultrasonic tip irrigation efficiency without any risk of propagation of dentin microcracks. They found that wall shear stress and apical pressure are affected by increasing the working length vapour volume fraction. However, root canal pressure does not contribute to dentin microcrack propagation. This finding provides valuable insight for clinical applications, ensuring safer and more effective endodontic procedures.
Root canal irrigation is essential for infection control during root canal treatment. Ultrasonic irrigation is a common method of root canal irrigation used in the clinical practice; however, the working length of ultrasonic tip can influence the fluid dynamics of the irrigant. Different from previous studies which often utilized simplified models, this study aims to utilize the computational fluid dynamic (CFD) and finite element method to evaluate the flow dynamics characteristics of the irrigation fluid when the ultrasonic tip was placed at different depths in the root canal and to predict crack extension during ultrasonic cleaning, based on the real tooth model. Images of the mandibular first premolar teeth were scanned using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), and then imported into the software for three-dimensional reconstruction. ICEM CFD 18.0 software was used to establish the root canal irrigation. The ultrasonic working tip was positioned at distances from the apex stop of 1 mm, 1.5 mm, 2 mm, 2.5 mm, and 3 mm (i.e., the five different working lengths of the working tip are 10 mm, 9.5 mm, 9 mm, 8.5 mm, and 8 mm) respectively. Irrigation velocity, wall shear stress and volume fraction in the root canal were visualized after setting the computing conditions. A dentin microcrack model was established by ABAQUS 6.14 software to predict crack extension during ultrasonic cleaning. Results: The CFD analysis showed that increasing the work length of the ultrasonic tip significantly increased vapor volume fraction, and wall shear stress, while reducing apical pressure. Notably, despite changes in the placement of the ultrasonic working tip, the velocity of irrigant always gradually decreases within the area 1 mm in front of the working tip. The pressure on the root canal significantly lower than the ultimate tensile strength of dentin. Increasing the working length can influence vapor volume fraction, wall shear stress and apical pressure. The pressure on the root canal does not cause the dentin microcrack propagation, in order to provide a reference for clinical application.
Reference:
Wu, W., Chen, Y., Tong, C. et al. The effect of ultrasonic tip working length on fluid dynamics in the root canal during the irrigation procedure: a computational fluid dynamics study. BMC Oral Health 25, 266 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-025-05620-3
Keywords:
Working Length, ultrasonic tip, impact, Root, Canal, Dynamics, BMC Oral Health, Wu, W., Chen, Y., Tong, C, Dentin microcrack, Working tip working length, Computational fluid dynamics analysis, Finite element analysis, Irrigation flow
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


