- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Carotid artery calcification in panoramic radiographs tied to oral infections and mortality: Study
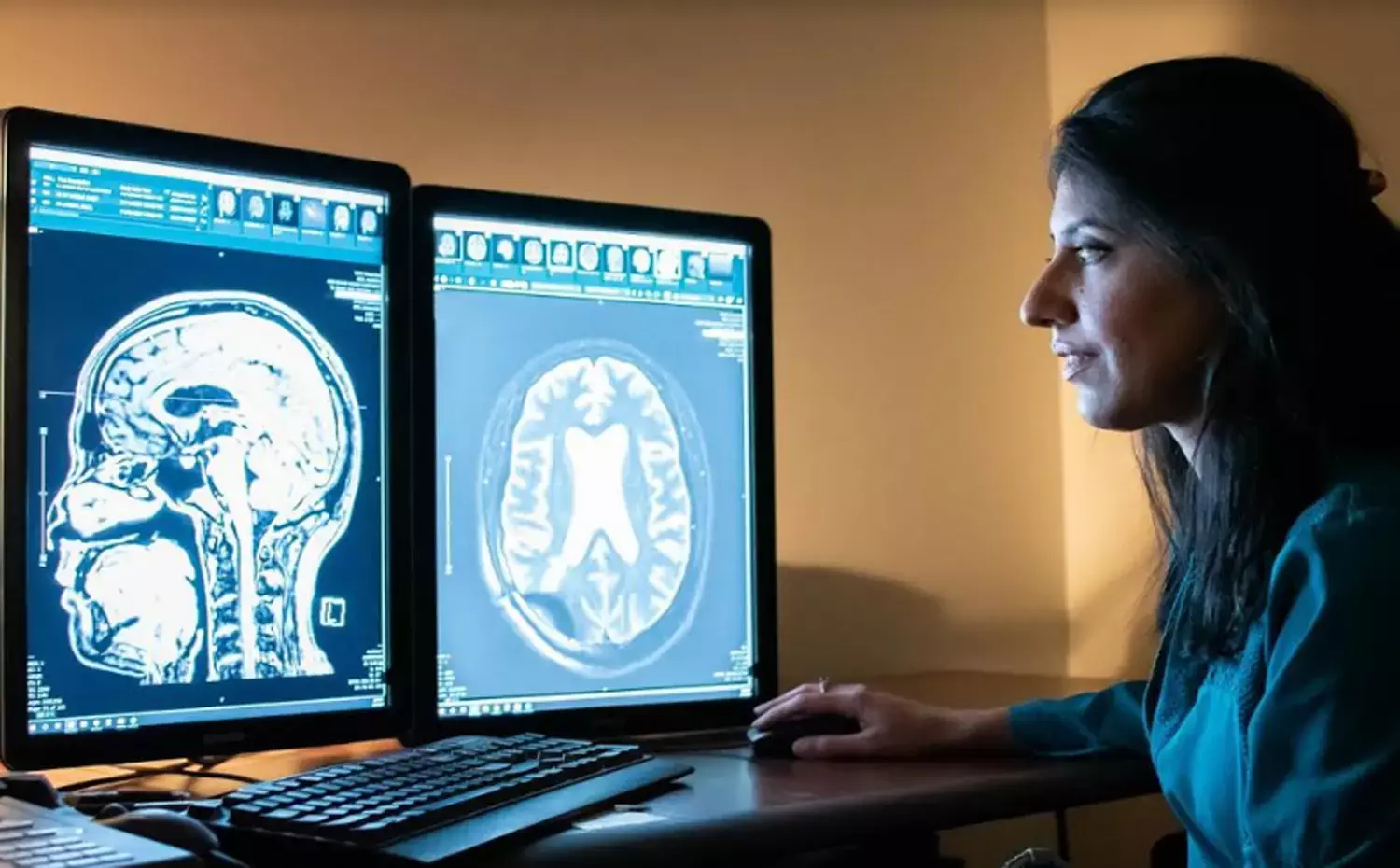
Recent research published in the International Endodontic Journal has brought into notice that carotid artery calcification (CAC) on panoramic tomography was associated with (i) apical and marginal periodontitis and dysbiotic bacterial species giving rise to an immunological response, and with (ii) severe, chronic CAD and increased mortality.
The authors, S. Paju and colleagues from the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland conducted the present study to assess the prevalence of carotid artery calcification (CAC) in relation to apical and marginal periodontitis, subgingival dysbiotic bacterial species and serum and saliva immune responses against them. In addition, the researchers also aimed was to analyse the association of CAC with angiographically verified coronary artery disease (CAD) and mortality.
In the present random Parogene cohort, the patients had an indication for coronary angiography. Apical and marginal periodontitis were diagnosed during clinical and radiographic oral examinations, and CAC on panoramic radiographs (n = 492).
Presence and severity of CAD were registered from angiography. Subgingival dysbiotic bacterial species were quantitated using checkerboard DNA‐DNA‐hybridization, and serum and saliva antibody levels were determined by immunoassays.
The cohort was followed‐up for 10 years or until death (median 9.9, range 0.21–10.4) via linkage to the national death register. The statistical models were adjusted for age, gender, smoking, hypertension, diabetes and dyslipidemia.
The results showed that-
a. A total of 102 (20.7%) patients had detectable CAC, which was moderate in 81 (16.4%) and severe in 21 (4.3%).
b. CAC was associated (OR, 95% CI) with severe apical periodontitis (2.25, 1.15–4.41), root canal fillings (1.15, 1.04–1.26), alveolar bone loss (2.66, 1.21–5.84), severe periodontal inflammation (2.23, 1.11–4.47), high level of gram‐negative subgingival species (2.73, 1.34–5.50), saliva IgG against dysbiotic species (1.05, 1.01–1.10/unit) and severe (2.58, 1.36–4.90) and chronic (2.13, 1.15–3.93) CAD.
c. A total of 105 (20.7%) patients died during the follow‐up and 53 (10.4%) deaths were because of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
d. Severe CAC predicted worse survival with HRs (95% CI) of 3.08 (1.58–6.06) for all‐cause and 3.43 (1.42–8.25) for CVD death.
Hence, the authors concluded that "CAC on panoramic tomography was associated with (i) apical and marginal periodontitis and dysbiotic bacterial species giving rise to an immunological response, and with (ii) severe, chronic CAD and increased mortality."
The results further emphasize the role of oral infections in coronary artery disease and the importance of referring a patient with CAC for a cardiovascular evaluation, they further added.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


