- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Certain salivary cytokines positively correlated with oral lichen planus severity: Study
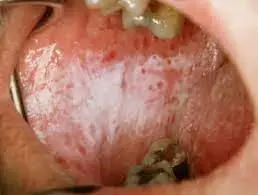
Certain salivary cytokines positively correlated with oral lichen planus severity, according to a recent study published in the Journal of Dental Sciences.
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic inflammatory lesion of oral mucosal, and its pathogenesis involves immune cell-mediated aberrances. However, the findings conflict with each other. This research aimed to comprehensively detect the salivary cytokine profile of patients with oral lichen planus (OLP).
The cohort included 60 Oral lichen planus (OLP) patients (30 reticular and 30 erosive), and 30 healthy controls, matched in age and sex. Human Cytokine/Chemokine Magnetic Bead Panel Kit (HCYTMAG-60K-PX41) was used to detect salivary inflammation-related cytokines. Rank sum test, group t-test, and ANOVA were used for data analysis in different groups. Moreover, Spearman's rank correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between salivary cytokine levels and Oral lichen planus (OLP) lesion severity.
The Results of the study are:
The levels of TNF-α, G-GSF, IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-8 were statistically significantly higher in both erosive and reticular OLP patients than in the healthy group, while the IL-13 level was significantly lower. Particularly, the salivary TNF-α, GM-CSF, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 levels were higher in the erosive Oral lichen planus (OLP) group than other groups. Spearman's rank correlation analysis revealed that the salivary TNF-α, GM-CSF, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, IL-1β and IL-6 levels were positively correlated with Oral lichen planus (OLP) lesion severity.
Thus, the researchers concluded that imbalance of the Th1/Th2-mediated immune response contributes to Oral lichen planus (OLP). Certain salivary cytokines, such as MIP-1α, MIP-1β, GM-CSF, and IL-6, are positively correlated with Oral lichen planus (OLP) severity, and they have a high potential as biomarkers to diagnose and predict Oral lichen planus (OLP) prognosis.
Reference:
Salivary cytokine profile in patients with oral lichen planus by Zheng-DaZhu et al. published in the Journal of Dental Sciences
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1991790221001240
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


