- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dental Radiographs effective in Detecting Pulp Stones, suggests study
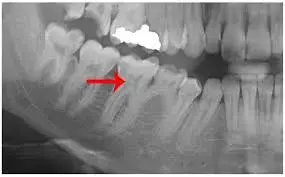
Researchers have found in a new study that radiographs are effective in detecting pulp stones. However, further research is needed to evaluate their potential as a screening tool for early detection of systemic diseases.
Dental pulp stones are distinct calcified bodies that can be found in teeth that are healthy, diseased, or even unerupted. Pulp stones are suggested to be a manifestation of various systemic and genetic diseases affecting different organs of the body.
Therefore, this study aimed to correlate the prevalence of pulp stones with gender, nationality, age, dental status, and systemic diseases. The medical records and radiographs of patients who visited the screening clinics and the Department of Oral Diagnosis at the College of Dentistry, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Dammam, Saudi Arabia, between January 2017 and June 2018 were analyzed in this study. Two examiners evaluated the digital orthopantomographs (OPGs) to identify the prevalence of pulp stones concerning the patient's age, gender, nationality, arch position, and medical condition. RESULTS: A total of 153 patient records were examined, and pulp stones were detected in 43.1% of the patients. Among the nationalities, Saudi patients were the most affected at 57.6%, while 42.4% were non-Saudi.
The maximum occurrence of pulp stones was observed in age group 4 (9.2%), while the minimum occurrence was in age group 8 (0.7%). The maximum occurrence of pulp stones (21.2%) was observed in age group 4 (36-45 years), while the minimum occurrence was 7.6% in age group 2 (16-25 years). Out of all examined patients, 46 (30.1%) patients were medically compromised. Among these medically compromised patients, radiographic examination showed that 56.5% (n=26) had pulp stones. This study supports the idea that dental radiographs are useful in detecting pulp stones. Further research is required to explore the potential of using dental radiographs as a screening tool for the early detection of systemic diseases.
Reference:
Fairozekhan, Arishiya T., et al. "Prevalence of Pulp Stones in Patients Visiting the Dental Hospital of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University: a Correlative Retrospective Study." Cureus, vol. 17, no. 1, 2025, pp. E77765.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


