- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Extensive surgery best option for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw
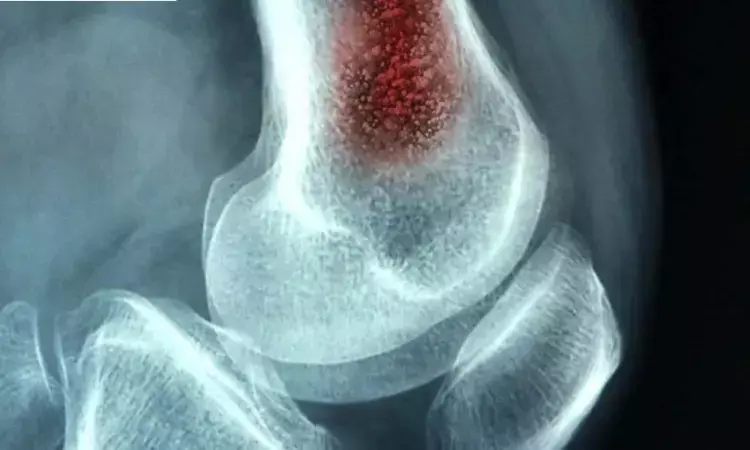
According to recent research, it has been observed that surgical treatment is an appropriate strategy for the management of maxillary MRONJ and complete resection of necrotic bone (i.e., extensive surgery) is needed to obtain complete healing of maxillary medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ).
The study is published in the Journal of Dental Sciences.
Because the anatomy and the nature of the bone tissue between the mandible and maxilla are largely different, more site-specific studies are required to improve the healing rate on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ).
Therefore, Kohei Okuyama and colleagues from the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan conducted the present study to assess maxillary MRONJ that was treated by surgery to understand its clinical characteristics, and to identify critical factors that influenced outcomes.
The medical records of 54 patients with maxillary MRONJ who underwent surgery were retrospectively reviewed. Variables related to the prognosis of MRONJ were extracted from the medical records and imaging, and were statistically analyzed.
The authors also evaluated the concomitant maxillary sinusitis (MS) after the surgical treatment of MRONJ, based on CT evaluation and change of symptoms.
The following findings were observed-
- The healing rate of surgery for maxillary MRONJ was 85.2%, which suggested that surgical treatment is an effective strategy for treating maxillary MRONJ.
- Multivariate analysis revealed that postoperative residual necrotic bone was a poor prognosticator for maxillary MRONJ.
- Among 10 patients who did not obtain healing of MS postoperatively, 8 patients showed an improvement.
Hence, the authors concluded that "surgical treatment is an appropriate strategy for maxillary MRONJ and complete resection of necrotic bone (i.e., extensive surgery) is needed to obtain complete healing of maxillary MRONJ. Concomitant MS tends to be healed or improved clinically in combination with the healing of maxillary MRONJ."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


