- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Full pulpotomy bests partial pulpotomy for managing of spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis: Study
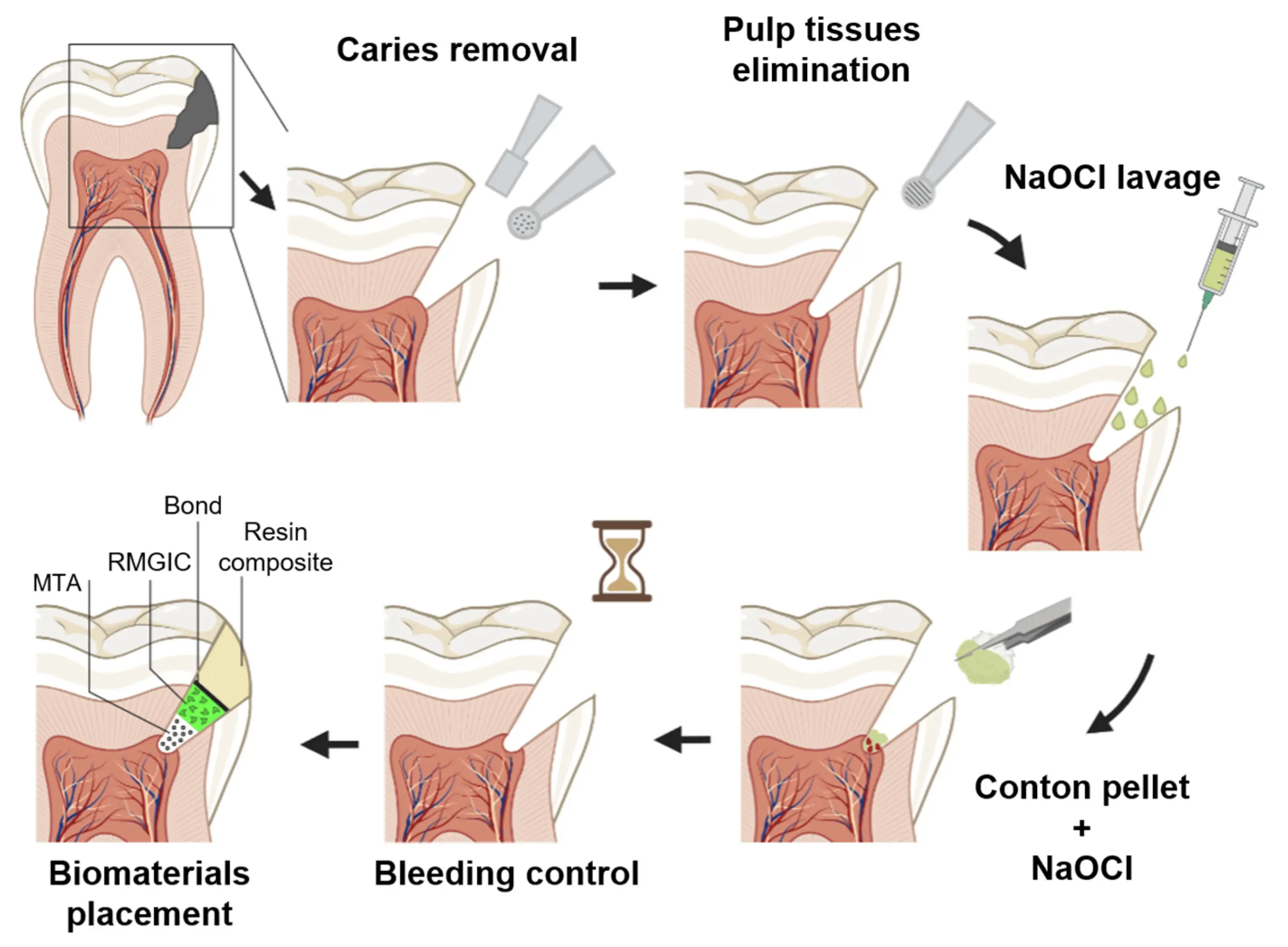
Full pulpotomy bests partial pulpotomy for managing spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis suggests a study published in the Journal of Endodontics.
The aim of this study was to compare the outcome and prognostic factors for partial and full pulpotomy in the management of mature teeth with spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis. The study was a parallel double blind randomized clinical trial, 200 carious mature permanent teeth with spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis were randomized using a block randomization technique to either partial pulpotomy (n=99) or full pulpotomy (n=101). Intraoperative assessment of the pulp under magnification was done, hemostasis was achieved with 2.5% NaOCl moist pellet, and NeoPUTTY was the pulpotomy material. Preoperative pain levels were recorded and revaluated after 1 week. Clinical and radiographic evaluation was done after 6 and 12 months. Data were analyzed using Chi-square, Wilcoxon rank tests and regression analysis.
Results: At 1week immediate failure occurred in 4 cases in partial pulpotomy, and 196/200 subjects reported pain relief and were satisfied with the treatment with no significant difference. At 6 months, 6 teeth failed in partial pulpotomy and 1 tooth in full pulpotomy, with a higher success rate for full pulpotomy (98.96 vs 89.69, p= 0.003). At 12 months the recall rate was 98% (96/200). Full pulpotomy was more successful than partial pulpotomy (98.98% (98/99), vs 84.53% (82/97), p< 0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed that the odds of success for full pulpotomy were 13.6 times higher than partial pulpotomy. Increased age and higher time to hemostasis were significantly associated with decreased odds of success. Full pulpotomy has higher success rate than partial pulpotomy in the management of spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis. Hemostasis within 4 minutes in partial pulpotomy can be set as cutoff point beyond which further tissue removal is indicated.
Reference:
Taha NA, Albakri SW. Outcome and prognostic factors for partial and full pulpotomy in the management of spontaneous symptomatic pulpitis in carious mature permanent teeth: A randomized clinical trial. J Endod. 2024 Apr 5:S0099-2399(24)00224-3. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2024.03.012. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38583758.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


