- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary habits linked to erosive tooth wear, reveals study
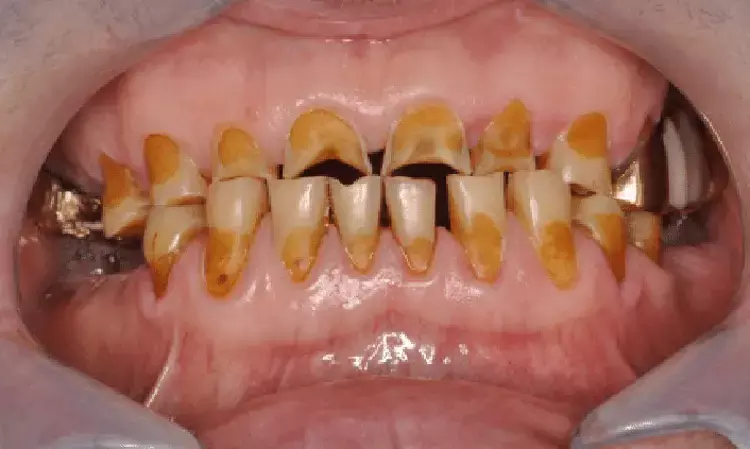
Gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary habits linked to erosive tooth wear reveal study published in the Journal of Dentistry.
Erosive tooth wear is a multifactorial condition. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to identify key risk factors for erosive tooth wear in permanent dentition.
Methodological quality and risk of bias were assessed using the modified Newcastle-Ottawa scale for cross-sectional studies. Risk factors were visually presented in a heatmap, and where possible, random-effects meta-analyses were performed for the odds ratios (ORs) of risk factors. A total of 87 publications reporting on 71 studies were included in the systematic review. The studies examined a variety of anamnestic risk factors (n = 80) that were categorized into ten domains (socio-demographics, socio-economics, general health, oral diseases, medication, oral hygiene, food, beverages, dietary habits, and leisure-related risk factors). Meta-analyses revealed significant associations between erosive tooth wear and male gender (padj.<0.001; OR=1.30, 95 % CI: 1.16–1.44), regurgitation (padj.=0.033; OR=2.27, 95 % CI: 1.41–3.65), digestive disorders (padj.<0.001; OR=1.81, 95 % CI: 1.48–2.21), consumption of acidic foods (padj.=0.033; OR=2.40, 95 % CI: 1.44–4.00), seasoning sauces (padj.=0.003; OR=1.28, 95 % CI: 1.13–1.44), nutritional supplements (padj.=0.019; OR=1.73, 95 % CI: 1.28–2.35), and carbonated drinks (padj.=0.019; OR=1.43, 95 % CI: 1.17–1.75). Most included studies exhibited low bias risk. Observational studies investigated a variety of anamnestic risk factors for erosive tooth wear. Future studies should employ validated questionnaires, particularly considering the most important risk factors. Erosive tooth wear is a prevalent condition. Clinicians should concentrate primarily on symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and dietary factors when screening patients at risk for erosive tooth wear.
Reference:
Felix Marschner, Philipp Kanzow, Annette Wiegand. Anamnestic risk factors for erosive tooth wear: Systematic review, mapping, and meta-analysis. Journal of Dentistry, Volume 144,
2024, 104962, ISSN 0300-5712, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2024.104962.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300571224001325)
Keywords:
Gastroesophageal, reflux disease, dietary habits, erosive, tooth wear,Journal of Dentistry,Felix Marschner, Philipp Kanzow, Annette Wiegand, Erosive tooth wear; Risk factors; Permanent dentition; Meta-analysis
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.


