- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Keratinized tissue width augmentation enhances clinical and esthetic outcomes using FGG and LCC
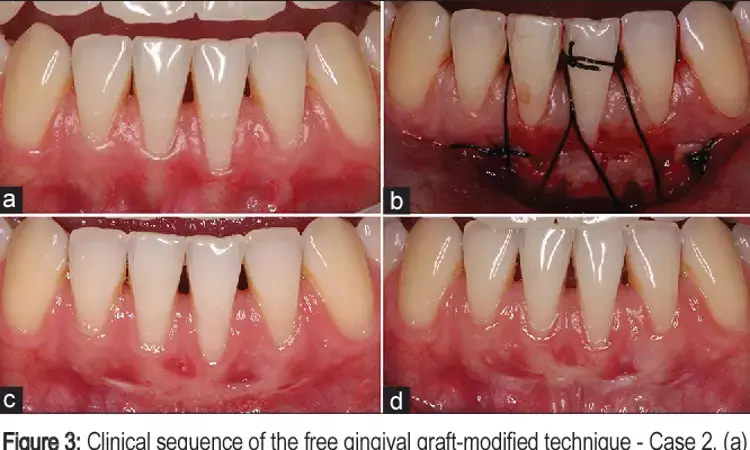
Keratinized tissue width augmentation enhanced clinical and esthetic outcomes using FGG and LCC suggests a recent study published in the Journal of Periodontology
A 13-year follow-up was conducted of a short-term investigation of the use of living cellular construct (LCC) versus free gingival graft (FGG) for keratinized tissue width (KTW) augmentation in natural dentition, to evaluate the long-term outcomes and assess the changes occurring since the end of the original 6-month study.
Twenty-four subjects out of the original 29 enrolled participants were available at the 13-year follow-up. The primary endpoint was the number of sites demonstrating stable clinical outcomes from 6 months to 13 years (defined as KTW gain, stability, or ≤0.5 mm of KTW loss, together with reduction, stability, or increase of probing depth, and recession depth [REC] ≤0.5 mm). Secondary outcomes included the assessment of KTW, attached gingiva width (AGW), REC, clinical attachment level, esthetics, and patient-reported outcomes at the 13-year visit, assessing the changes from baseline to 6 months.
Results
Nine sites per group (42.9%) were found to have maintained stable (≤0.5 mm or improved) clinical outcomes from 6 months to 13 years. No significant differences were observed for the clinical parameters between LCC and FGG from 6 months to 13 years. However, the longitudinal mixed model analysis showed that FGG delivered significantly better clinical outcomes over 13 years (p < 0.01). LCC-treated sites exhibited superior esthetic outcomes compared to FGG-treated sites at 6 months and 13 years (p < 0.01). Patient-evaluated esthetics were significantly higher for LCC over FGG (p < 0.01). Patient overall treatment preference was also in favor of LCC (p < 0.01).
A similar stability of the treatment outcomes from 6 months to 13 years was found for LCC- and FGG-treated sites, with both approaches shown to be effective in augmenting KTW and AGW. However, superior clinical outcomes were found for FGG over 13 years, while LCC was associated with better esthetics and patient-reported outcomes than FGG.
Reference:
Tavelli, L, Barootchi, S, Rodriguez, MV, et al. Living cellular constructs for keratinized tissue augmentation: A 13-year follow-up from a split-mouth randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2023; 1- 13. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.23-0040
Keywords:
Keratinized, tissue, width, augmentation, enhanced, clinical, esthetic, outcomes, using, FGG, LCC, Journal of Periodontology, Tavelli, L, Barootchi, S, Rodriguez
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


