- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Physiological Simulated Decalcifying Agent effective in decalcification of pulp stones: study
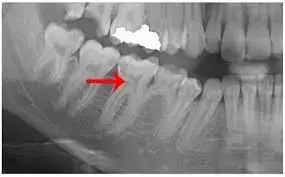
Physiological Simulated Decalcifying Agent is efficacious in the decalcification of pulp stones suggests a recent study published in the Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
Despite constant advances in science, obscurity remains in the efficient removal of pulp stones to aid in successful root canal treatment. In this context, chemical means of dissolving pulp stones were explored.
The aim of this study is to evaluate and to compare the efficacy of decalcifying agents on the dissolution of pulp stones. The study was divided into two groups for pulp stone analysis (21 samples) and dentin analysis (54 samples). Twenty-one pulp stones from patients aged 18–70 who underwent root canal treatment were collected and divided into three subgroups (n = 7) randomly. They were subjected to chemical treatment in a labeled glass container with 5 ml of the respective chemical agents, such as 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution (positive control), no treatment (negative control), and newly developed Physiological Simulated Decalcifying Agent (PSDA). At the end of the study period (24 h), the samples were removed, rinsed with deionized water, and subjected to physical analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Energy –dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. Under dentin analysis, 54 maxillary premolars scheduled for orthodontic extraction without caries or extensive restorations were selected, following which 2-mm thick transverse dentinal sections at the cementoenamel junction level were obtained and randomly divided into two groups for SEM (n = 21) and microhardness analysis (n = 33). The samples were subjected to respective chemical treatment groups similar to pulp stones for 24 h and analyzed using SEM, EDS, and microhardness analysis.
The Results of the study are:
- Postchemical treatment with the newly developed decalcifying solution, the pulp stones showed the absence of nodular crystallites and surface softening under SEM and a decrease in the calcium level under EDS analysis.
- Concerning the microhardness of dentin, no significant changes could be observed.
Thus, the newly explored Physiological Simulated Decalcifying Agent was found to be efficacious in the decalcification of pulp stones at a clinically relevant time of 24 h, without significantly affecting the structural integrity and the hardness values of dentin.
Reference:
Kavimalar Ravichandran et al. Comparative evaluation of decalcifying agents for dissolution of pulp stones: An in vitro study. DOI: 10.4103/jcd.jcd_35_22
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


