- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Postoperative pain intensity same with use of NaOCl or other irrigation solutions: Study
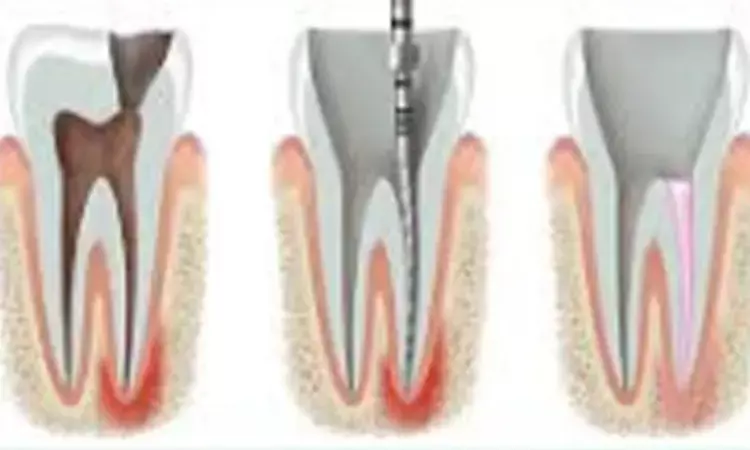
Researchers have recently observed that there was no significant difference in the presence of postoperative pain between the 8.25% NaOCl and the other irrigation solutions.
The study is published in the Journal of Endodontics.
Postoperative pain is common after endodontic treatment, so it is very important for the dentist to control this pain as well as to know how widespread the problem is. Root canal treatment must be carried out taking into account that instrumentation and obturation techniques can provoke periapical damage.
Luciana Stadler Demenech and colleagues from the School of Health Sciences, Universidade Positivo, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil carried out the present study with the aim to evaluate the postoperative pain in patients after endodontic treatment using 8.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) compared with other concentrations and 2% chlorhexidine (CHX).
In this double-blind randomized trial, the authors evaluated a total of 180 patients who underwent a single session of endodontic treatment under irrigation with 2.5%, 5.25%, or 8.25% NaOCl or 2% CHX solutions.
The presence of postoperative pain was assessed 24, 48, and 72 hours after treatment and recorded using the visual analog scale (VAS). A descriptive analysis, logistic regression, and Wald test were performed.
The following results were seen-
- Altogether 169 patients participated, of whom 107 were women, and the mean age was 38.1 ± 14.4 years.
- No significant differences occurred between the irrigants and the pain outcomes, not even for the use of postoperative pain medication and responses to VAS (P > .05).
- In the multivariate model including irrigants, after 24 hours or at any time, a significant difference (P < .05) remained in preparation time ≥10 minutes and the presence of overfilling.
- Also, in relation to the VAS, the overfilling presented significantly different results (P < .05).
Hence, the authors concluded by saying that "there was no significant difference in the presence of postoperative pain between the 8.25% NaOCl and the other irrigation solutions. However, the extended preparation time and the overfilling material were responsible for the increase of postoperative pain."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


