- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pressed lithium disilicate successful in long-term esthetic restoration of tooth wear, finds research
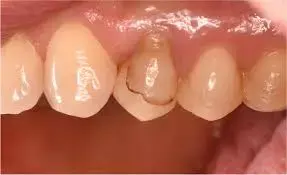
Pressed lithium disilicate successful in long-term esthetic restoration of tooth wear, finds research published in the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.
Long-term clinical data are lacking on the comparative survival of adhesively luted lithium disilicate glass-ceramic complete and partial coverage restorations in patients with severe wear and the effect that different clinical variables have on their survival. The purpose of this study was to examine the 14-year survival of pressed e.max lithium disilicate glass-ceramic complete and partial coverage restorations in patients with severe wear and to evaluate associated clinical parameters. Patients demonstrating severe wear and requiring single unit defect-specific partial or complete coverage restorations were recruited in a clinical private practice and received lithium disilicate restorations. The effect of various clinical parameters was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier survival curves to account for attrition bias and other causes of failure.
The statistical significance of differences between parameters was determined by using the log rank test (α=.05). Results: A total of 53 participants (24 men and 29 women) requiring 662 lithium disilicate restorations were evaluated. The mean age of the participants at the time of restoration placement was 60 (range 25 to 85 years). Of 662 units, 551 were anterior and posterior complete and 111 were posterior partial coverage restorations. Six failures (bulk fracture or large chip) requiring replacement occurred with the average time to failure of 4.5 (range 2 to 8) years, yielding a crude estimate of annual failure of 0.1% (cumulative monitoring period of 4650 years, overall survival rate of 98.6%).
Of the 551 complete coverage restorations, 4 failed (0 anterior, 4 posterior), yielding a crude estimate of 0.1% annual failure with the survival function time at 14 years. Of the 111 partial coverage restorations, 2 failed, yielding a crude estimate of 0.4% annual failure with the survival function time at 12 years. The only statistically significant difference was seen between anterior crowns and posterior onlays, with no failures in anterior crowns (P<.001). Other clinical variables had no significant effect on survival (P>.05). Pressed e.max lithium disilicate partial and complete coverage restorations both showed high survival rates in patients with severe wear over 14 years with an overall yearly failure rate of 0.1%. Risk of failure at any age was minimal for both men and women. All anterior crowns survived. The highest annual failure rate (0.4%) was for posterior onlay partial coverage restorations.
Reference:
Margvelashvili-Malament M, Thompson V, Polyakov V, Malament KA. Over 14-year survival of pressed e.max lithium disilicate glass-ceramic complete and partial coverage restorations in patients with severe wear: A prospective clinical study. J Prosthet Dent. 2024 Jul 30:S0022-3913(24)00464-5. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2024.06.031. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39084921.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


