- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intralesional Hyaluronidase Shows Promise in Treating Fibrosis in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Case Report
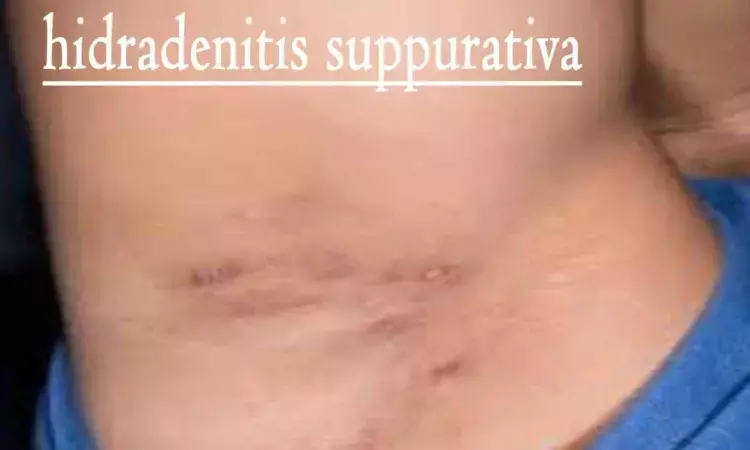
Turkey: In a notable advancement for dermatology, a recent case report has highlighted the potential of intralesional hyaluronidase as a treatment for fibrosis associated with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). Published in the International Journal of Dermatology, the report details a case where this novel approach successfully reduced fibrotic tissue in a patient with this chronic inflammatory skin condition.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by painful nodules, abscesses, and scarring, primarily affecting areas with apocrine glands such as the armpits, groin, and buttocks. Fibrosis, the thickening and hardening of tissue, is a common complication that can exacerbate symptoms and hinder treatment effectiveness.
The release of follicular contents due to blockage in the pilosebaceous unit caused by hyperkeratosis leads to subsequent rupture, initiating the inflammatory process. Overactivation of the inflammatory pathway, aberrant cytokine signaling, and inflammasome activation contribute to and perpetuate the proinflammatory cascade. Research suggests that fibroblast activation and inflammatory cytokines may be pivotal in understanding the causes and developing targeted treatments. Disruption of the skin microbiome is also implicated in the pathogenic process of HS. The inflammatory response triggered by internal and external stimuli subsequently activates fibroblasts, contributing to excessive and abnormal fibrosis in affected tissues.
In the case, Recep Dursun, Department of Dermatology, Necmettin Erbakan University Faculty of Medicine, Konya, Turkey, and colleagues aimed to present the successful treatment outcome of the administration of intradermal hyaluronidase, which can be an alternative in supportive treatment for fibroblasts and the fibrosis the patient developed.
The case concerns a 26-year-old woman with Hurley stage 3 hidradenitis suppurativa, presented with deep and painful lesions with discharge and scars between her breasts. The patient received intradermal hyaluronidase treatment in five sessions, spaced 14 days apart, totaling 2500 IU. Additionally, they were prescribed oral clindamycin at a dose of 300 mg/day and topical clindamycin.
Following 2.5 months, the patient showed significantly improved scar reduction, inflammatory lesions, and improvements in symptoms. No treatment-related complications were noted.
To conclude, hyaluronidase may be a safe, minimally invasive, and comfortable treatment option for fibrosis in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa; however, there is a need for more comprehensive studies.
Reference:
Dursun, R., Altay, E., & Temiz, S. A. Intralesional hyaluronidase as a treatment for fibrosis in hidradenitis suppurativa: A case report. International Journal of Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.17312
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


