- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
5 Percent Spironolactone Shows Significant Acne Reduction and Strong Safety Profile: Meta-Analysis
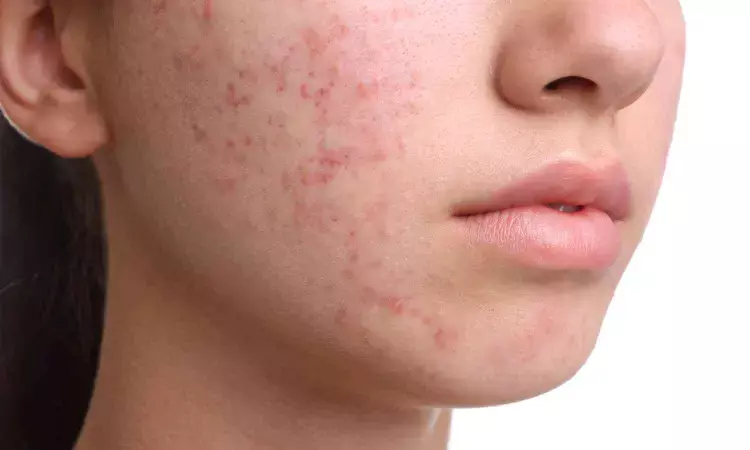
Egypt: A recent systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of spironolactone in patients with acne vulgaris suggests that the drug significantly improves acne severity while maintaining an excellent safety profile. The meta-analysis of 1,086 patients found that spironolactone 5% significantly reduced acne lesion count (MD −6.85) and acne severity index (MD −6.33) compared to placebo.
"The 100 mg oral dose demonstrated greater ASI improvement than topical treatments. While reductions in comedones and pustules were modest within 6–8 weeks, notable improvements emerged after eight weeks, with an excellent safety profile," the researchers reported in Archives of Dermatological Research.
The researchers note that acne vulgaris affects approximately 9% of the global population, with a higher prevalence among women, often impacting their quality of life. While topical treatments are commonly used for mild cases, systemic therapies are essential for managing moderate to severe acne. Spironolactone, an androgen receptor inhibitor, shows potential for treating severe acne, though conclusive evidence remains limited.
Against the above background, Mohamed A. Alsaied, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt, and colleagues performed a meta-analysis using R software to evaluate total lesion count, acne severity score, adverse events, and the mean number of comedones, papules, and pustules. The search process identified 14 studies involving a total of 1,086 participants.
The following were the key findings of the meta-analysis:
- Spironolactone 5% demonstrated greater efficacy than placebo in reducing total lesion count (MD −6.85) and acne severity index (ASI) (MD −6.33).
- The 100 mg oral dose showed significantly greater ASI improvement than the topical group.
- A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials found no significant reduction in comedones and pustules within 6–8 weeks.
- Single-arm studies reported notable improvements in comedones and pustules after eight weeks of treatment.
The meta-analysis demonstrated that 5% spironolactone significantly reduced total lesion count and acne severity index after eight weeks, with notable improvements in comedones and papules, while maintaining an excellent safety profile. However, the limited number of eligible studies and reliance on single-arm data highlight the need for further randomized controlled trials. Experts emphasize that future research should focus on large-scale RCTs comparing spironolactone with standard acne treatments to determine its long-term efficacy and optimal dosage.
"With its strong safety profile and significant impact on acne severity, spironolactone holds promise as a widely accepted treatment option for patients with persistent acne," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Farrag, M., Abo Elnaga, A.A., Alsaied, M.A. et al. Efficacy and safety of Spironolactone in treating patients with acne vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1,086 patients. Arch Dermatol Res 317, 328 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-025-03815-w
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


