- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Breakthrough in Melasma Treatment: Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser Emerges as Top Choice
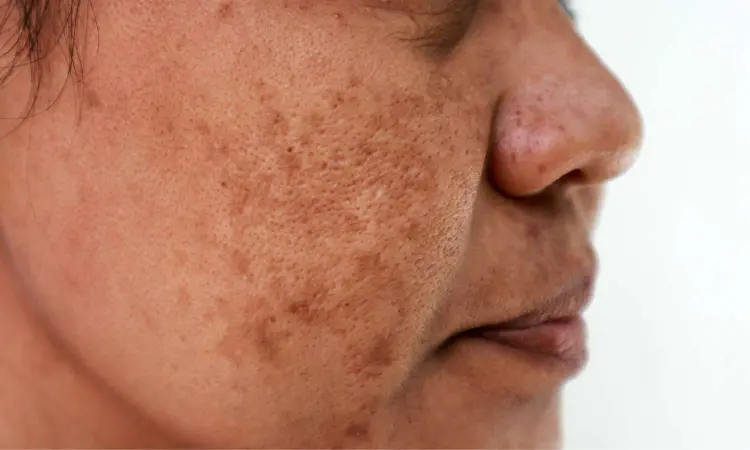
Melasma, a challenging hyperpigmentation disorder, often poses therapeutic dilemmas due to its intricate pathogenesis, recurrence tendencies, and substantial morbidity impact. In a bid to revolutionize treatment outcomes, a comprehensive network meta-analysis (NMA) has scrutinized various laser-related therapies, shedding light on the most effective approaches for managing melasma.
This study was published in Journal Of Cosmetic Dermatology by Wenyi and colleagues. A comprehensive meta-analysis of 39 clinical studies, involving 1394 participants, has shed light on the most effective laser-related therapies for treating melasma. The study compared various approaches, revealing that Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with topical medications (QSND+TM) stands out as the top choice, significantly improving the melasma area severity index (MASI) score. Other notable contenders include oral tranexamic acid (oTA), microneedling with topical medications (MN+TM), Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with intense pulse light (QSND+IPL), and fractional carbon dioxide laser with topical medications (FCDL+TM).
- Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser Dominates:
Superior Efficacy: The NMA unequivocally establishes the supremacy of Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with topical medications (QSND+TM). Its efficacy outshines Q-switched Nd:YAG laser alone, Er:YAG laser with topical medications, and picosecond laser with topical medications.
Significant Improvement: QSND+TM led to a notable decrease in the melasma area severity index (MASI) score, highlighting its prowess in addressing hyperpigmentation.
- Microneedling Excels:
Effective Combination: Microneedling with topical medications (MN+TM) emerges as a formidable contender, surpassing picosecond laser and standalone topical medications.
Enhanced Curative Efficacy: MN+TM demonstrates superiority in improving the MASI score, presenting itself as a promising choice for melasma treatment.
- Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) Rankings:
QSND+TM claims the top spot with an impressive SUCRA value of 85.9%, indicating its high efficacy.
Other noteworthy contenders include oral tranexamic acid (oTA), MN+TM, QSND+IPL, and fractional carbon dioxide laser with topical medications (FCDL+TM).
- Clinical Recommendations:
First-Line Choice: The study recommends Qs-Nd:YAG laser with topical medications as the primary therapeutic choice, considering its top-ranking SUCRA value and significant efficacy.
Preferred Combination: MN+TM stands out as the superior choice among modalities like PICO and standalone topical medications, emphasizing its potential for enhancing curative outcomes.
- Considerations for Clinical Decision-Making:
Adverse Effects: Clinical decisions should weigh the adverse effects of each modality, ensuring a tailored approach to patient care.
Patient Characteristics: The patient's skin type, duration of the disease, and other relevant factors should inform the selection of the most suitable treatment strategy.
This meta-analysis not only advances our understanding of melasma treatment but provides clinicians with a roadmap for precision care. Armed with these insights, dermatologists can navigate the complex landscape of melasma therapeutics, offering patients tailored solutions for improved outcomes.
Reference:
Ma, W., Gao, Q., Liu, J., Zhong, X., Xu, T., Wu, Q., Cheng, Z., Luo, N., & Hao, P. Efficacy and safety of laser‐related therapy for melasma: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology,2023;22(11):2910–2924. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.16006
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


