- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Clindamycin and rifampicin addition to adalimumab benefit patients with hidradenitis suppurativa with draining tunnels
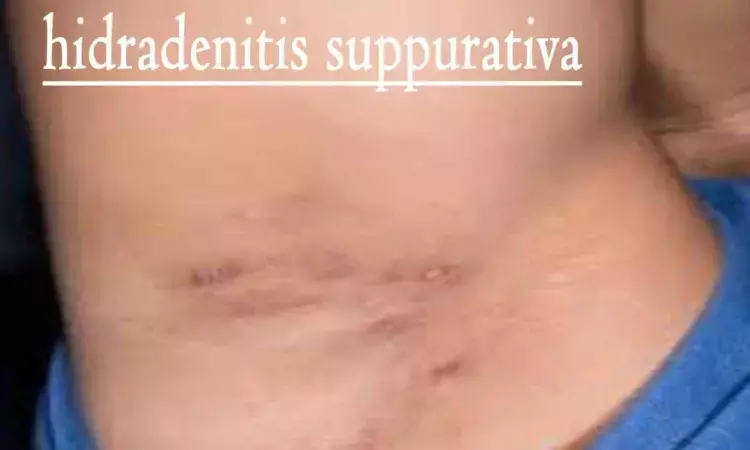
Netherlands: A recent study published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology showed improved clinical effectiveness of adalimumab when initiated with clindamycin and rifampicin in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
The researchers revealed greater clinical effectiveness of adalimumab initiated with clindamycin and rifampicin than adalimumab monotherapy. An important difference was observed in the effect of the decrease of draining tunnels, addressing a serious limitation of adalimumab monotherapy.
"The initiation of HS treatment with the combination of adalimumab with rifampicin and clindamycin showed greater clinical effectiveness than adalimumab monotherapy as measured by the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4; −55), Hidradenitis Suppurativa Physician's Global Assessment scale (HS-PGA), pain, draining tunnels and Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR)," the researchers reported.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic, debilitating, inflammatory skin disease, that primarily manifests in the inverse body sites. Distinctive features are abscesses, inflammatory nodules, and draining tunnels which can result in pruritus, pain, suppuration and malodor, causing a significant reduction in the patient's quality of life.
Adalimumab monotherapy for HS is often insufficient with a maximum clinical efficacy of 60% in HiSCR and limited effect on draining tunnels. Data indicate that adalimumab therapy could be improved by concomitant antibiotics.
P. Aarts, Department of Dermatology, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, and colleagues aimed to compare the clinical effectiveness of adalimumab with clindamycin and rifampicin versus adalimumab monotherapy after 12 weeks in a retrospective study.
The study included patients who started adalimumab with additional rifampicin and clindamycin and patients treated with adalimumab monotherapy, matched on sex and refined Hurley score. The primary outcome measure of the study was the difference in change in the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System at 12 weeks.
The study led to the following findings:
- 62 patients were included in the combination therapy group (n = 31) and adalimumab monotherapy group (n = 31), showing comparable IHS4 scores; 32.5 versus 29 at baseline respectively.
- The combination therapy demonstrated greater clinical effectiveness expressed in median IHS4 improvement (−20 versus −9), IHS4-55 (74% versus 36%), median draining tunnel reduction (−4 versus −2,) and pain response (47% versus 27%,).
"Our study shows significantly greater effectiveness when adalimumab is initiated with rifampicin and clindamycin compared with adalimumab monotherapy," the researchers wrote. "Therefore, we would recommend the clindamycin and rifampicin addition to adalimumab therapy during the first 12 weeks of treatment, specifically in patients with draining tunnels."
Reference:
Aarts, P., & Prens, E. P. Improved clinical effectiveness of adalimumab when initiated with clindamycin and rifampicin in hidradenitis suppurativa. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.19725
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


