- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Cysteamine 5 Percent Cream: A Promising Alternative to Hydroquinone for Melasma Management, Research Reveals
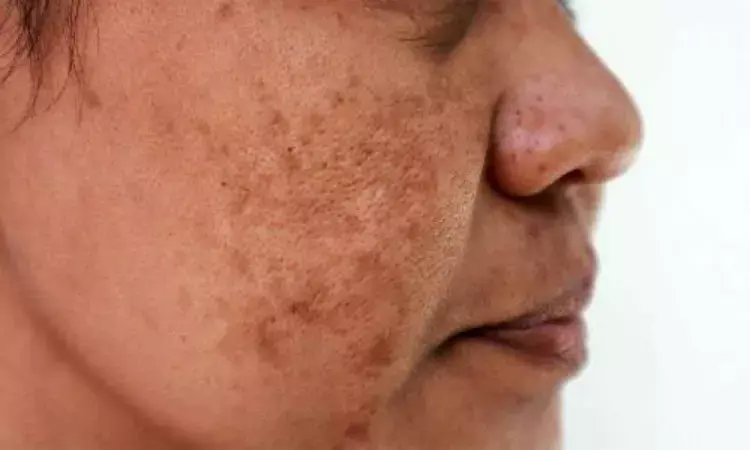
Indonesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials have highlighted the efficacy and safety of cysteamine 5% cream in managing melasma, offering a potential alternative to the widely used topical hydroquinone.
The study, published in the Archives of Dermatological Research, indicated that cysteamine 5% cream could serve as a viable alternative to topical hydroquinone for managing melasma, offering comparable efficacy and safety.
Melasma, a common hyperpigmentation disorder, often presents as dark, irregular patches on the face and affects quality of life. While hydroquinone has been the standard treatment for decades, concerns about its long-term safety and tolerability have spurred the search for effective alternatives.
Cysteamine 5% cream has emerged as a promising candidate. This topical formulation harnesses cysteamine, a naturally occurring compound, to reduce melanin production in the skin. Unlike hydroquinone, which has been associated with side effects like irritation and ochronosis, cysteamine offers a comparable efficacy profile with potentially fewer risks.
Against the above background, Ferra Olivia Mawu & Paulus Mario Christopher from Sam Ratulangi University/R. D. Kandou Hospital, Manado, North Sulawesi, Indonesia, aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of cysteamine 5% cream in managing melasma.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a comprehensive search across Europe PMC, Medline, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library databases up to June 22, 2024. The review included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared cysteamine with placebo or hydroquinone in patients with melasma. To analyze the outcomes, random-effect models were employed to determine the odds ratio and standardized mean difference (SMD). A total of seven RCTs were included in the analysis.
The following were the key findings:
- Cysteamine 5% cream was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing the Melasma Area and Severity Index (SMD −0.84).
- There was no significant difference in efficacy between cysteamine 5% and hydroquinone 4% (SMD 0.16).
- The incidence of adverse events (AEs) such as erythema, irritation, burning, itching, and dryness was higher with cysteamine 5% compared to a placebo.
- The occurrence of adverse events was similar between cysteamine 5% and hydroquinone 4%.
Despite the promising findings, the authors emphasize the need for further research, particularly large-scale studies, to establish cysteamine’s long-term safety and effectiveness across diverse populations. Continued exploration could also identify optimal treatment protocols, enhancing its integration into standard melasma management practices.
As melasma remains a challenging condition to treat, the emergence of cysteamine 5% cream represents an encouraging development. Its potential to provide a safe, effective, and well-tolerated solution offers hope to millions of individuals seeking relief from this persistent skin condition.
Reference:
Mawu, F.O., Christopher, P.M. Efficacy and safety of cysteamine 5% cream for the management of melasma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Dermatol Res 317, 117 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-024-03571-3
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


