- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dietary elimination method might improve severe atopic dermatitis symptoms
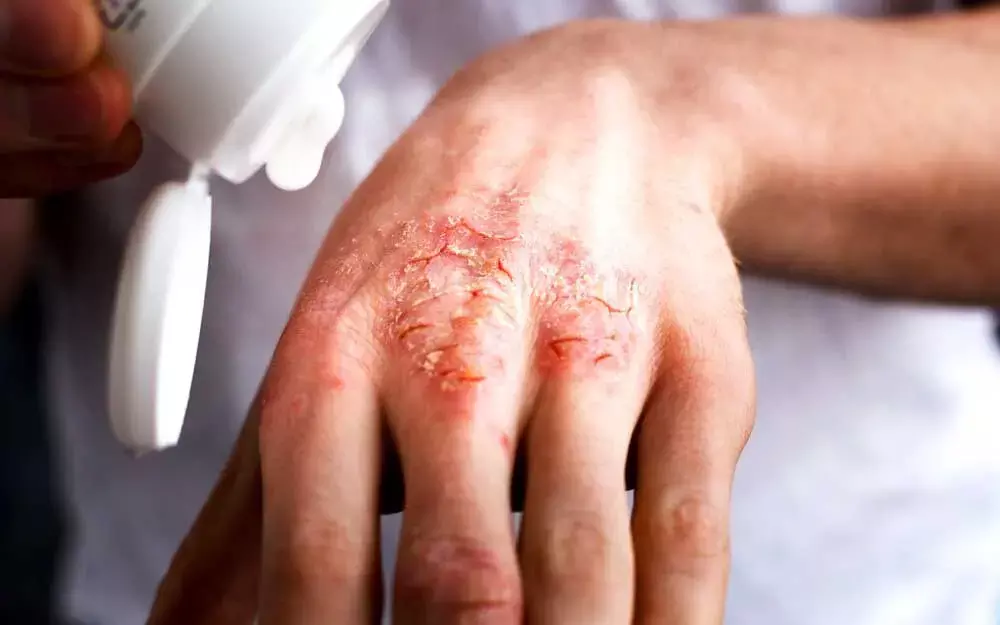
In individuals with mild to severe atopic dermatitis (AD), dietary elimination may result in a minor, possibly insignificant reduction in the severity of the eczema, pruritus, and insomnia, says an article published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
Skin infections and atopic comorbidities are frequently linked to atopic dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by relapsing or persistent pruritus, skin discomfort, lichenification, excoriation, xerosis, and dyspigmentation. Disease activity is thought to be influenced by a variety of factors, such as immune dysregulation, skin barrier dysfunction, and microbial dysbiosis due to internal and external factors. Paul Oykhman and colleagues did this study to comprehensively analyze the advantages and disadvantages of dietary removal for the treatment of AD.
Without regard to language restrictions, we searched MEDLINE, AMED, Embase, PsycINFO, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies contrasting dietary elimination and no dietary elimination for the treatment of AD from the beginning to January 18, 2022. Also carried out were random-effects meta-analyses of eczema outcomes. To rate the degree of evidence's certainty, the development, assessment, and evaluation approach was used.
The key findings of this study were:
1. This meta-analysis included ten RCTs.
2. Low-certainty data suggested that food elimination may only modestly lessen eczema severity, pruritus, and insomnia when compared to no dietary elimination.
3. Based on elimination strategy (empiric vs. guided by testing) or food-specific sensitization, there were no discernible subgroup differences.
4. Although there is indirect evidence that suggests elimination diets may raise the risk of developing IgE-mediated food allergies, there was insufficient data on the negative effects of elimination diets among the included RCTs.
The Authors suggest that dietary elimination should be weighed against the risks of indiscriminate elimination diets, which include the possibility of developing IgE-mediated food allergies and foregoing more potent AD treatments.
Reference:
Oykhman, P., Dookie, J., Al-Rammahy, H., de Benedetto, A., Asiniwasis, R. N., LeBovidge, J., Wang, J., Ong, P. Y., Lio, P., Gutierrez, A., Capozza, K., Martin, S. A., Silverberg, J. I., Schneider, L., & Chu, D. K. (2022). Dietary Elimination for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. In The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice (Vol. 10, Issue 10, pp. 2657-2666.e8). Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2022.06.044
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


