- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dyslipidemia associated with Lichen Planus may need Comprehensive Management: Study
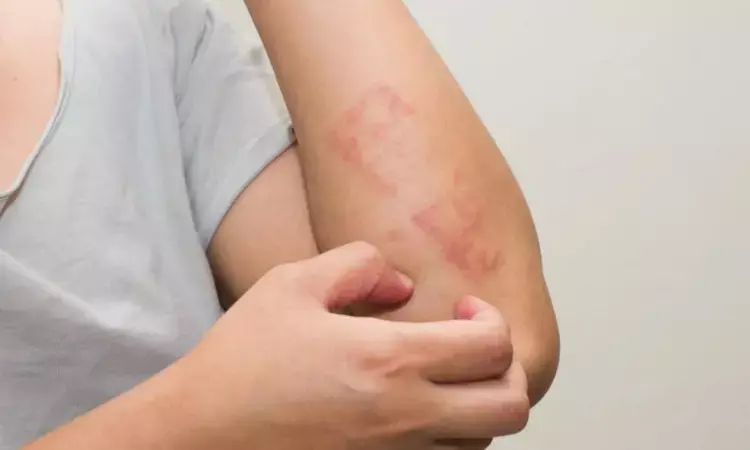
A new study published in the journal of Cureus revealed that Lichen Planus (LP) patients show increased lipid levels and associated comorbidities, emphasizing the importance of routine lipid profile monitoring, early intervention, and lifestyle modification counselling to reduce dyslipidemia and cardiovascular risks.
Flat-topped, violaceous, itchy, polygonal papules that are often bilateral and symmetrical and most frequently seen on the extremities are the characteristic cutaneous presentation of LP. Antioxidant systems are also significantly disrupted in lichen planus, which causes oxidative stress and damages proteins, DNA, and lipids. However, it is widely acknowledged that persistent dyslipidemia and oxidative stress raise the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Numerous investigations have documented a probable correlation between dyslipidemia and lichen planus, indicating a potential relationship between metabolic disorders and this chronic inflammatory illness. Existing data has revealed inconsistent outcomes across various groups. Thus, this study by Jeyraveena and colleagues was set to learn more about the connection between dyslipidemia and lichen planus.
From August 2022 to August 2024, comparative cross-sectional research was carried out at Chennai's Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research. Nearly, 67 clinically confirmed LP patients and 67 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were included in the research. Fasting lipid levels and thorough clinical tests were carried out. Descriptive statistics, paired t-tests, and chi-square tests were among the statistical methods used.
Both male and female patients with LP had statistically significant higher levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and total cholesterol (p=0.001) than controls. However, only male LP patients had substantially higher triglyceride levels (p=0.04). The two groups' levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) were comparable. LP patients also had greater rates of cardiovascular illness, diabetes, hypothyroidism, and hypertension. The prevalence of dyslipidemia was positively connected with the length of sickness.
Overall, this study found that both male and female lichen planus patients had significantly higher levels of total cholesterol and LDL and that male LP patients had raised triglycerides. Nonetheless, there was no discernible difference in the overall prevalence of dyslipidemia. This seeming contradiction raises the possibility of a link between lipid metabolic abnormalities and the chronic inflammatory state of LP.
Source:
N M, J., Vidhya H, M., Sundaram, M., Rangarajan, S., & Swaminathan, A. (2025). Association between dyslipidemia and lichen planus: A cross-sectional study in a tertiary care hospital. Cureus, 17(4), e82401. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.82401
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


