- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
High-dose clobetasol propionate safe and effective treatment for cutaneous lichen planus, study finds
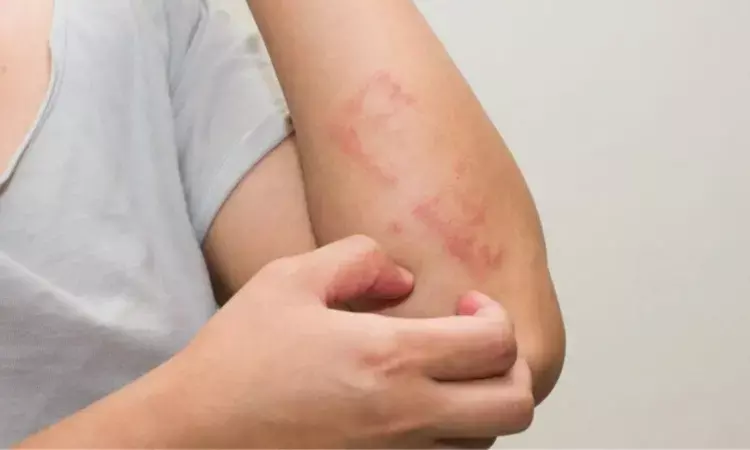
France: High-dose clobetasol propionate 0.05% is a well-tolerated, effective and easy-to-implement treatment for cutaneous lichen planus, according to results from a single-centre retrospective cohort study published in The Journal of Dermatology.
"Superpotent topical corticosteroids are as effective (if not more) as traditional systemic treatments (e.g. acitretin and methotrexate) for cutaneous lichen planus, with a better side-effect profile without the requirement of laboratory monitoring," the researchers wrote in their study.
Cutaneous lichen planus is a highly pruritic dermatosis with an unmet need for its management. Audrey Melin and the research team aimed to evaluate the short-term tolerance and effect of 0.05% clobetasol propionate's high doses in cutaneous lichen planus.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted the study from 2017 to 2021. It included all adults treated with clobetasol propionate 0.05%'s high-dose of >5 g/day for cutaneous lichen planus. Those having less than 10% affected body surface area at initial presentation or who were administered concomitant systemic therapy were not included.
The complete remission rate by the 16th week was determined (primary endpoint). Secondary endpoints included pruritus reduction, maximum daily and median cumulative doses, and occurrence of adverse events. A total of 57 patients (mean age 48 years; 60% females) were included. At initial presentation, cutaneous lichen planus was present for two months and involved a median body surface area of 27%.
Key findings include:
- At week 16, 72% of patients had achieved complete remission without treatment modification, among whom 61% had achieved it at week 6. The median daily and cumulative doses were 20 g/day and 560 g.
- Three patients experienced mild adverse events.
- No statistical association was demonstrated between the duration of the disease before treatment initiation and clinical response.
"For cutaneous lichen planus, high-dose clobetasol propionate 0.05% seems to be an effective, well-tolerated, and easy-to-implement treatment," the researchers concluded.
About Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a condition that can cause irritation and swell in the hair, skin, nails and mucous membranes. Lichen planus usually appears as itchy, purplish, flat bumps on the skin that develop over several weeks. In the vagina, mouth, and other areas covered by a mucous membrane, lichen planus forms lacy white patches, sometimes with painful sores.
The first-line treatments of cutaneous lichen planus include topical steroids, specifically class I or II ointments. A second choice would be systemic steroids for symptom control and more rapid resolution. Intramuscular triamcinolone 40-80 mg is preferred by many practitioners every 6-8 weeks. In some patients, oral metronidazole is shown to be an effective therapy. In published studies, oral acitretin is reported to be effective. Owing to the lack of experience, many other treatments, including mycophenolate mofetil, are of uncertain efficacy.
Reference:
Melin A, Bouchereau S, Guelimi R, Bergqvist C, Condamina M, Giraud-Kerleroux L, Hirsch G, Hua C, Wolkenstein P, Skayem C, Le Cleach L. Safety and efficacy of high-dose clobetasol propionate 0.05% in cutaneous lichen planus. J Dermatol. 2022 Dec 28. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16689. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36578108.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


