- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ligelizumab improves sleep interference in chronic spontaneous urticaria patients
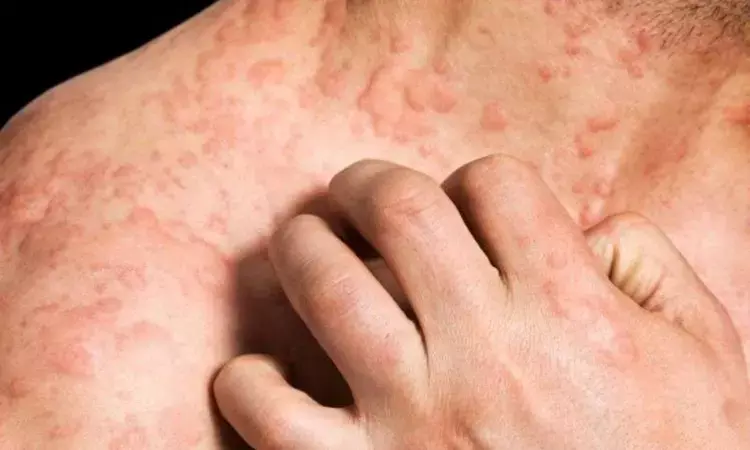
Germany: Ligelizumab demonstrated effective and persistent responses in managing sleep interference in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) patients, as well as quantitatively greater responses than omalizumab and placebo, says an article published in the journal Clinical and Translational Allergy. Treatment of CSU symptoms with ligelizumab improved health-related quality of life (HRQoL), illness burden, and sleep quality significantly.
CSU has a detrimental influence on patients' sleep, lowering their health-related quality of life. Half of the patients with poorly managed CSU report sleep disruption on a regular or nightly basis, which can contribute to sadness, social, anxiety, and work-related issues. A Giménez-Arnau and team present a sub-analysis of the Phase 2b core trial and the extension study to compare sleep, activity interference, dermatological quality of life, and job effect in patients with CSU treated with omalizumab and ligelizumab with placebo.
The adult patients in this randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, Phase 2b core trial (NCT02477332) had moderate to severe CSU that had not been well managed with H1-antihistamines. The current study included patients who were randomly assigned to receive ligelizumab 72 or 240 mg, omalizumab 300 mg, or placebo every 4 weeks for five injections over 20 weeks, with a 24-week treatment-free follow-up. If their weekly urticaria activity score was 12, patients may enter the open-label extension trial (NCT02649218) from Week 32 onwards, which comprised an open-label therapy (52 weeks of ligelizumab 240 mg q4w) and a 48-week post-treatment follow-up. Weekly Sleep Interference Scores (AIS7), overall work impairment, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores were all calculated.
The key findings of this study are as follow:
1. The treatment arms' mean baseline SIS7 scores for omalizumab 300 mg (n = 85), ligelizumab 72 mg (n = 84) and 240 mg (n = 85), and placebo (n = 43) were balanced.
2. By Week 12, patients' sleep interference had significantly improved, with a least square mean (standard error) increase from baseline (CFB) in SIS7 of -7.84, -7.55, -6.98, and -5.85, respectively.
3. CFB in AIS7 were -8.25, -8.25, -7.30 (0.60), and -5.62 by Week 12, DLQI scores were -9.79, -9.93, -8.35, and -6.99, and Overall Work Impairment scores were 28.96, 30.76, 25.74, and 20.13 for ligelizumab 72 and 240.
In conclusion, sleep disruption is a significant and clinically important symptom of CSU that is generally overlooked. As part of an integrated treatment strategy, patient assessments of the effect of therapy on sleep quality should be clearly included.
Reference:
Giménez-Arnau, A, Maurer, M, Bernstein, J, et al. Ligelizumab improves sleep interference and disease burden in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Clin Transl Allergy. 2022;e12121. https://doi.org/10.1002/clt2.12121
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


