- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Low dose cyclophosphamide pulses decrease skin sclerosis in systemic sclerosis: IJDVL study
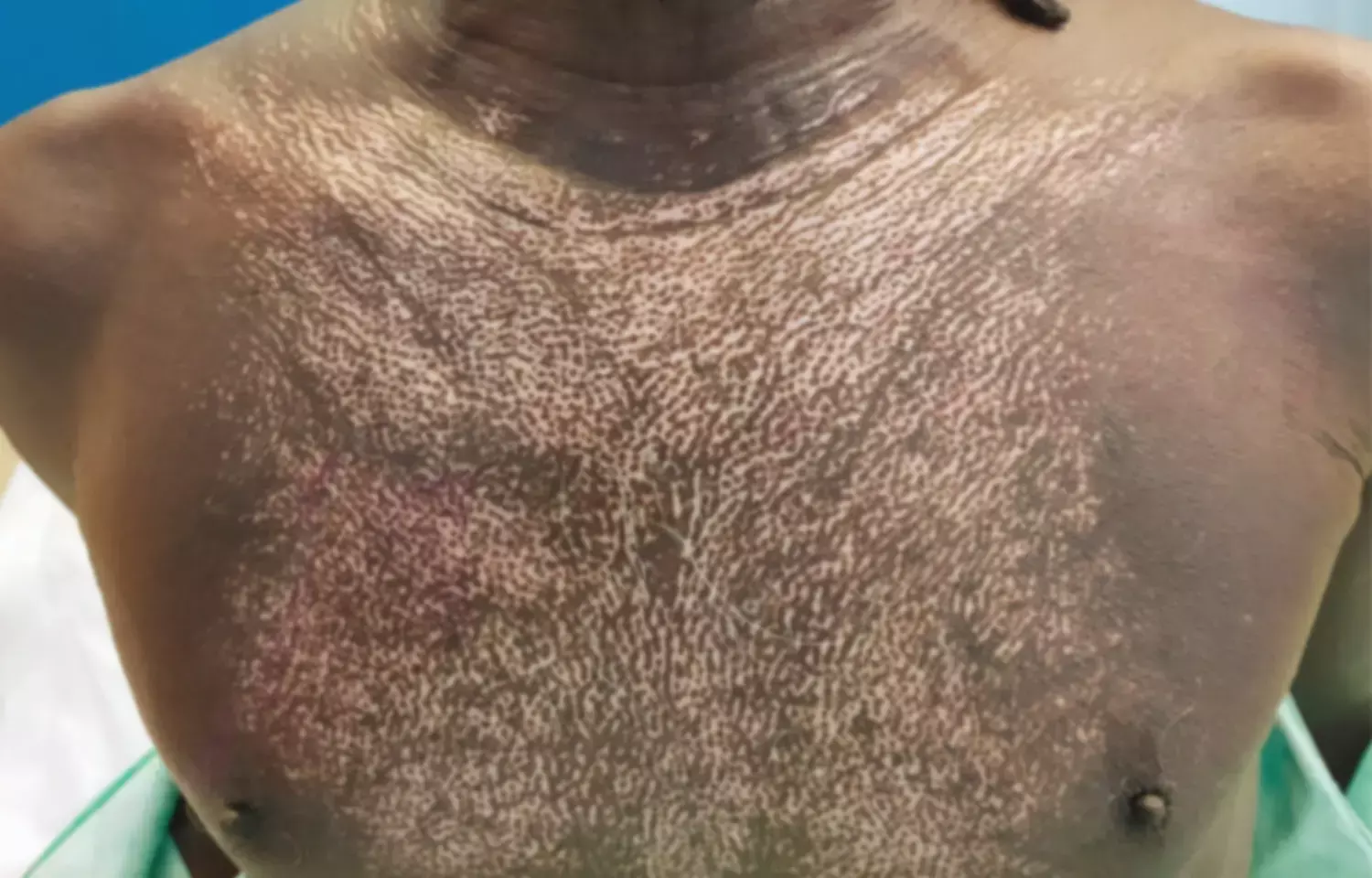
Source NEJM
Low dose cyclophosphamide pulses decreases skin sclerosis in systemic sclerosis finds IJDVL study. Systemic sclerosis is a connective tissue disease with considerable morbidity and mortality. The decrease in skin sclerosis has a positive effect on the quality of life but only few controlled clinical trials have been done on treatment of skin sclerosis due to the rarity of the disease and its highly variable course. Recently a study demonstrating the efficacy of low dose cyclophosphamide on skin sclerosis in both limited and diffuse types of systemic sclerosis was published in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology.
This was a single‑center open‑label interventional study including all diagnosed cases of systemic sclerosis as per the American College of Rheumatology (1980) criteria from the period January 2015 through December 2017.
Exclusion criteria included- grade IV dyspnoea,cyanosis, severe restrictive lung disease (Forced vital capacity of ≤50% predicted), echocardiogram abnormalities, diffuse infiltrative opacities in chest radiography, patients in renal crisis, patients on treatment with prednisolone or other immunosuppressive agents and those who have not completed their family
Intravenous cyclophosphamide 500 mg in 500 mL 5% dextrose over 2 h once in a month and supportive treatment including vasodilators was administered to all the patients for 6 months with adequate measures to reduce bladder toxicity. Modified Rodnan skin score (mRss) was assessed at the starting and the end of the treatment at six months. Sclerosis was assessed separately at different sites before and after treatment with monitoring for any adverse effects.
Results
Total 36 patients were enrolled in the study of which 34 were women. The mean age of patients was 45 ± 9.7 years (range: 29-67 years). The mean duration of disease was 6 years ± 5.1 years (range: 6 months-20 years). Of 36, 20 patients (55.5%) had limited cutaneous type and 16 patients (44.4%) had diffuse cutaneous type of disease.
The most common sclerosed site was the fingers followed by the forearm, face and feet. Severe sclerosis of grade three was detected on the fingers in a majority (79.4%) but with less severe involvement on the forearms and dorsa of hands. The mRss of 36 patients ranged from 5 to 33 with a mean value of 19 ± 6.8. Two patients failed to complete six months of treatment.
The mean mRss before and after cyclophosphamide therapy at six months in 34 patients demonstrated a significant reduction from 18.7 ± 6.9 to 12.8 ± 7.2 (P < 0.001). There was a significant reduction of mRss in limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis from 16.5 ± 6 to 10 ± 5.2 (P < 0.001) and in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis from 21.9 ± 7 to 16.8 ± 8 (P = 0.003). In patients with mRss < 18 score, mean mRss reduced from 13.7 ± 4.1 to 9.3 ± 4.2 (P < 0.001). In patients with a mRss ≥ 18, the mean mRss decreased from 24.4 ± 4.6 to 16.8 ± 8 (P < 0.001).
Reduction in mRss was noticed from two months of starting the treatment. A significant reduction in mean sclerosis was found at all sites except on both arms. The right and left forearm and right fingers showed the maximum response.
Improvement of dyspnoea and arthralgia was seen in 10/13 patients (77%) and 8/9 patients (88.9%) respectively. The reduction in incidence of Raynauds phenomenon, healing of fingertip ulcers and reduction in recurrence of leg ulcerations was observed in 21/26 patients (80.8%), 14/20 patients (70%) and 6/7 patients (85.7%) respectively. There was no improvement in pigmentation and exacerbation of gastroesophageal symptoms in a majority (20/22) of patients at the end of six months.
Some common adverse effects observed were vomiting, transient elevation of liver enzymes, temporary amenorrhea, generalized itching and gingival hyperplasia but none of them were serious enough to discontinue treatment.
In conclusion this study shows that a low dose intravenous cyclophosphamide monthly pulse for a short duration is well tolerated and produces a significant reduction of skin sclerosis in both limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis with more severely affected distal extremities responding earlier than less severely affected proximal parts. It is even effective in reducing the skin sclerosis in patients with low baseline mRss or milder skin fibrosis who are likely to progress.
Source- Khader A, Valiaveetil B, Nalini SD, George B, Sasidharanpillai S, Nazeer MM, et al. Effect of monthly cyclophosphamide pulses on skin sclerosis in systemic sclerosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2021;87:728-31.
MBBS
Dr Manoj Kumar Nayak has completed his M.B.B.S. from the prestigious institute Bangalore medical college and research institute, Bengaluru. He completed his M.D. Dermatology from AIIMS Rishikesh. He is actively involved in the field of dermatology with special interests in vitiligo, immunobullous disorders, psoriasis and procedural dermatology. His continued interest in academics and recent developments serves as an inspiration to work with medical dialogues.He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


