- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
NAC-GED 5% gel promising treatment option for moderate to severe acne
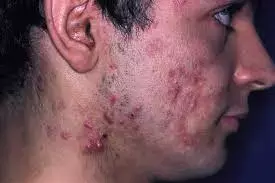
A promising treatment option is NAC-GED 5% gel for moderate to severe acne, according to a recent study published in the British Journal of Dermatology.
Preliminary in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ modulator N-acetyl-GED-0507-34-LEVO (NAC-GED) for the treatment of acne-stimulating sebaceous cell differentiation. Effectiveness of. It improves sebum composition and controls the inflammatory process.
A group of researchers conducted a study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of NAC-GED (5% and 2%) in patients with moderate to severe facial crusts Vulgaris.
This double-blind phase II randomized controlled trial was conducted at 36 sites in Germany, Italy, and Poland. Patients aged 12-30 years with facial acne, Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score 3-4, inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions 20-100 years (2% or 5%) were randomly assigned to topical application of study drug or placebo. . vehicle), once a day for 12 weeks. Primary efficacy endpoints were rate of change in total disease count (TLC) from baseline and the 12-week IGA success rate. Safety endpoints were adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs.
The results of the survey are as follows.
• Between Q1 2019 and Q1 2020, 450 patients had NAC-GED 5% (n = 150), NAC-GED 2% (n = 150), or vehicle (n =). Randomly assigned. up to 150).
• The rate of change in TLC reduction was statistically significantly higher in both the NAC-GED 5% and NAC-GED 2% groups compared to vehicles.
• A greater percentage of patients treated with NAC-GED 5% experienced IGA success compared to the vehicle group.
• The success rate of IGA in the 2% NAC-GED group was 33%.
• The proportion of patients with one or more AEs in the NAC-GED group was 5%, NAC-GED 2% and vehicles were 19%, 16% and 19%, respectively.
Therefore, topical application of NAC-GED 5% reduced TLC, increased the success rate of IGA, and could be safely used in patients with scaly plaques. Therefore, the new PPARγ modulator, NAC-GED, showed an effective clinical response.
Reference:
Picardo, M., Cardinali, C., La Placa, M., Lewartowska-Białek, A., Lora, V., Micali, G., Montisci, R., Morbelli, L., Nova, A., Parodi, A., Reich, A., Sebastian, M., Turek-Urasińska, K., Weirich, O., Zdybski, J., Zouboulis, C.C. and (2022), Efficacy and safety of N-acetyl-GED-0507-34-LEVO gel in patients with moderate-to-severe facial acne vulgaris: a phase IIb randomized double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.21663
Keywords:
Mauro Picardo, Carla Cardinali, Michelangelo La Placa, Anita Lewartowska-Białek, Viviana Lora, Giuseppe Micali, Roberta Montisci, Luca Morbelli, Andrea Nova, Aurora Parodi, Adam Reich, Michael Sebastian, Katarzyna Turek-Urasińska, Oliver Weirich, Jacek Zdybski, Christos C. Zouboulis, the GEDACNE Study Group, Efficacy, safety, N-acetyl-GED-0507-34, LEVO, gel, patients, moderate-to severe, facial, acne, vulgaris, phase IIb, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial, British Journal of Dermatology
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


