- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Psoriasis in hypertension patients significantly increases mortality risk, claims study
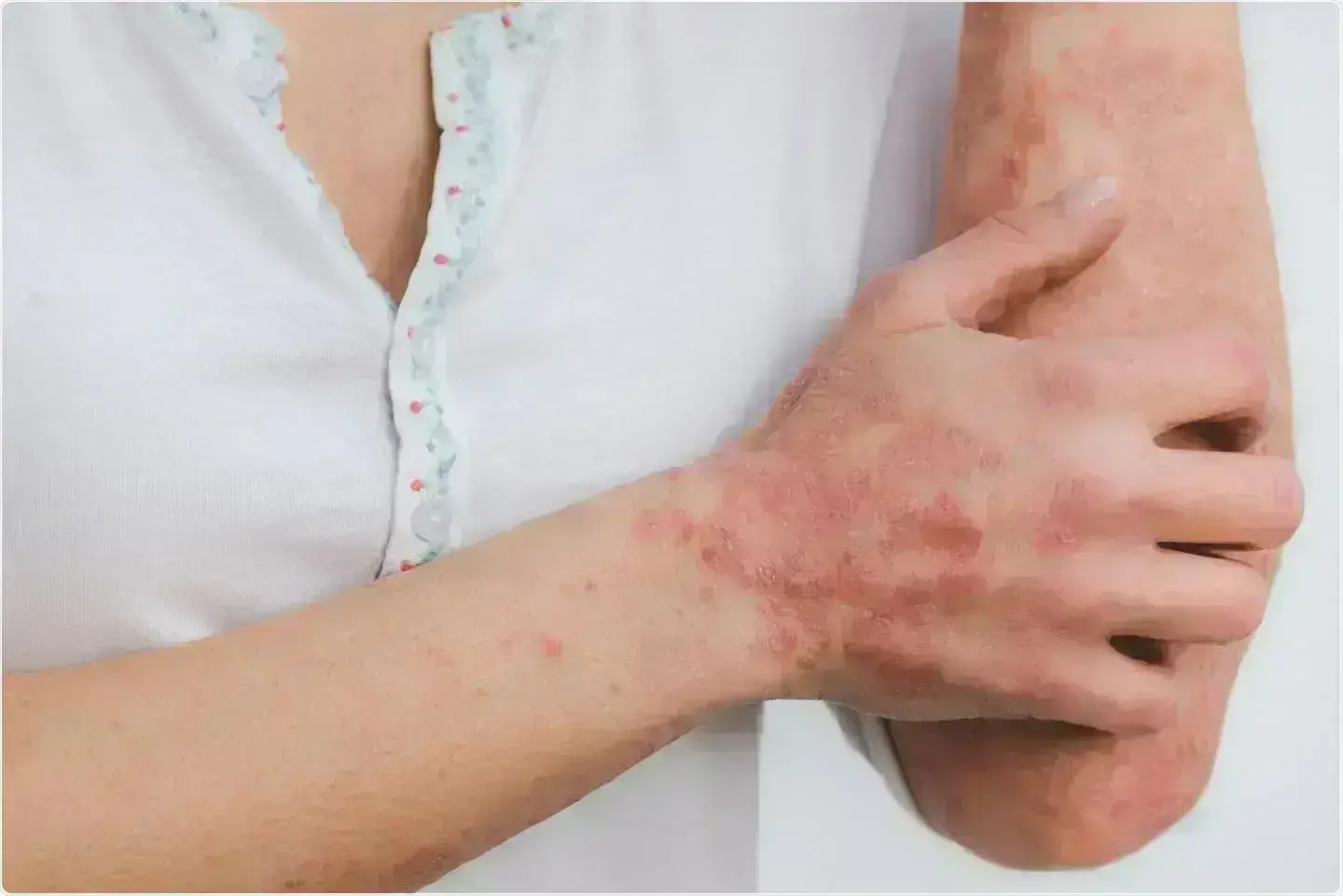
Psoriasis in hypertension patients significantly increases mortality risk, claims study published in PLoS One.
The linkage between psoriasis and hypertension has been established through observational studies. Despite this, a comprehensive assessment of the combined effects of psoriasis and hypertension on all-cause mortality is lacking. The principal aim of the present study is to elucidate the synergistic impact of psoriasis and hypertension on mortality within a representative cohort of adults residing in the United States. The analysis was conducted on comprehensive datasets derived from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study spanning two distinct periods: 2003–2006 and 2009–2014. The determination of psoriasis status relied on self-reported questionnaire data, whereas hypertension was characterized by parameters including systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg, diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg, self-reported physician diagnosis, or the use of antihypertensive medication.
The assessment of the interplay between psoriasis and hypertension employed multivariable logistic regression analyses. Continuous monitoring of participants’ vital status was conducted until December 31, 2019. A four-level variable amalgamating information on psoriasis and hypertension was established, and the evaluation of survival probability utilized the Kaplan-Meier curve alongside Cox regression analysis. Hazard ratios (HRs) and their associated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were computed to scrutinize the correlation between psoriasis/hypertension and all-cause mortality. Results: In total, this study included 19,799 participants, among whom 554 had psoriasis and 7,692 had hypertension.
The findings from the logistic regression analyses indicated a heightened risk of hypertension among individuals with psoriasis in comparison to those devoid of psoriasis. Throughout a median follow-up spanning 105 months, 1,845 participants experienced all-cause death. In comparison to individuals devoid of both hypertension and psoriasis, those with psoriasis alone exhibited an all-cause mortality HR of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.35–1.53), individuals with hypertension alone showed an HR of 1.78 (95% CI: 1.55–2.04), and those with both psoriasis and hypertension had an HR of 2.33 (95% CI: 1.60–3.40). In the course of a stratified analysis differentiating between the presence and absence of psoriasis, it was noted that hypertension correlated with an elevated risk of all-cause mortality in individuals lacking psoriasis (HR 1.77, 95% CI: 1.54–2.04). Notably, this association was further accentuated among individuals with psoriasis, revealing an increased HR of 3.23 (95% CI: 1.47–7.13). The outcomes of our investigation demonstrated a noteworthy and positive association between psoriasis, hypertension, and all-cause mortality. These findings indicate that individuals who have both psoriasis and hypertension face an increased likelihood of mortality.
Reference:
Zhao H, Wu J, Wu Q. Synergistic impact of psoriasis and hypertension on all-cause mortality risk: A prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 2024;19(7):e0306048. Published 2024 Jul 5. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0306048
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


