- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ritlecitinib safe treatment option for alopecia areata in adults and adolescents: Lancet
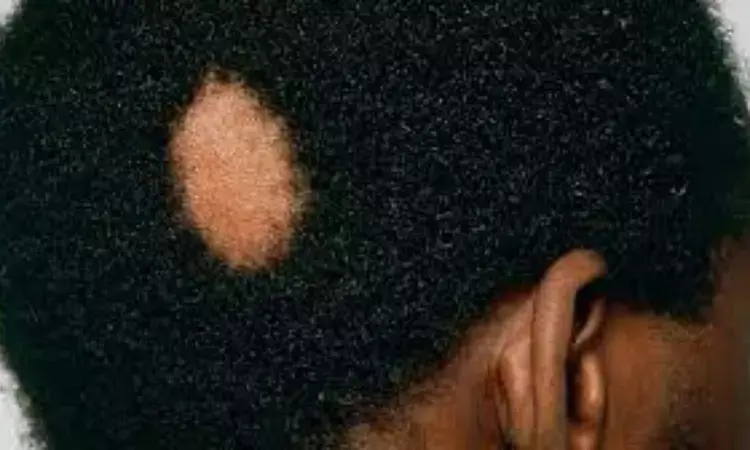
USA: A recent study published in The Lancet has projected ritlecitinib to be an appropriate treatment option for alopecia areata in individuals who are candidates for systemic therapy.
The study found Ritlecitinib to be well tolerated and effective in patients aged 12 and above with alopecia areata. Ritlecitinib is an oral, selective dual JAK3/TEC family kinase inhibitor.
Alopecia areata is characterised by non-scarring scalp, body, or face hair loss. Brett King, Department of Dermatology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA, and colleagues investigated the safety and efficacy of ritlecitinib in patients with alopecia areata in a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2b–3 trial.
The study was conducted at 118 sites across 18 countries and involved patients aged 12 years and above with alopecia areata and at least 50% scalp hair loss. They were randomly assigned to o oral ritlecitinib or placebo once daily for 24 weeks, with or without a 4-week loading dose (loading dose of 50 mg, 30 mg, 10 mg, 200 mg followed by a loading dose of 50 mg, or 200 mg followed by 30 mg), followed by an extension of 24 weeks, during which ritlecitinib groups continued their assigned amounts. Patients assigned to the initial placebo switched to 50 mg or 200 mg ritlecitinib loading dose followed by 50 mg.
The patients, sponsors, and investigators were masked for treatment, and all patients received the same amount of tablets to maintain masking. Regardless of whether they received treatment, the primary endpoint was evaluated in all assigned patients. A SALT score of 20 or below was determined at week 24 (primary endpoint).
The study led to the following findings:
·1097 patients were screened between 2018 and 2021, and 718 were randomly allocated to receive ritlecitinib 200 mg + 30 mg (n=130), 200 mg + 50 mg (n=132), 30 mg (n=132), 50 mg (n=130), 10 mg (n=63), placebo to 200 mg + 50 mg (n=65), or placebo to 50 mg (n=66).
· 104 patients discontinued treatment of 718 patients randomly assigned (34 withdrew, 19 adverse events [AEs], 12 physician decisions, 12 lack of efficacy, 13 lost to follow-up, five rolled over to long-term study transfer, two protocol deviations, four pregnancies, one declined to attend follow-up due to COVID-19, one non-compliance, and one attended last visit very late due to COVID-19).
· At week 24, 31% of 124 patients in the ritlecitinib 200 mg + 50 mg group, 22% of 121 patients in the group of 200 mg + 30 mg, 23% of 124 patients in the 50 mg group, 14% of 119 patients in the 30 mg group, and in the placebo group 2% of 130 patients had a response based on SALT score 20 or below.
· Response rate differences based on the SALT score of 20 or below between the placebo and the ritlecitinib 200 mg + 50 mg group was 29·1%, 20·8% for the 200 mg + 30 mg group, 21·9% for the 50 mg group, and for the 30 mg group, it was 12·8%.
· Up to week 48 and including the follow-up period, adverse events had been reported in 82% of 131 patients in the ritlecitinib 200 mg + 50 mg group, 81% of 129 patients in the 200 mg + 30 mg group, 85% of 130 patients in the 50 mg group, in the 30 mg group, 80% of 132 patients, in the 10 mg group 76% of 62 patients, in the extension period 83% of 65 patients placebo to ritlecitinib 200 mg + 50 mg, and 86% of 66 patients in the placebo to 50 mg group.
· Between groups, the incidence of each adverse event was similar, and there were no deaths.
Ritlecitinib was well tolerated and effective in patients aged 12 and older with alopecia areata.
"Compared to placebo, Ritlecitinib 30 mg and 50 mg daily (with or without a 4-week 200 mg loading dose) led to significant hair regrowth," the researchers wrote. "Over 48 weeks, Ritlecitinib had a favourable safety profile, and no major adverse cardiovascular events, deaths, or opportunistic infections were reported."
Reference:
King, B., Zhang, X., Harcha, W. G., Szepietowski, J. C., Shapiro, J., Lynde, C., Mesinkovska, N. A., Zwillich, S. H., Napatalung, L., Wajsbrot, D., Fayyad, R., Freyman, A., Mitra, D., Purohit, V., Sinclair, R., & Wolk, R. (2023). Efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib in adults and adolescents with alopecia areata: A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2b–3 trial. The Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00222-2
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


