- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
selumetinib effective, safe in kids with symptomatic and inoperable plexiform neurofibromas
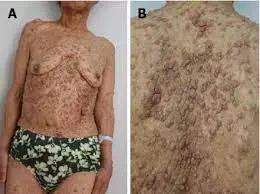
Selumetinib is effective and safe in children with symptomatic and inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN), according to a recent study published in Neurology.
Although the recent approval of selumetinib is expected to transform the management of children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), particularly those with symptomatic and inoperable plexiform neurofibromas, no systematic review has summarized its efficacy and safety based on the latest studies. This study was conducted to systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of selumetinib in children with NF1.
Original articles reporting the efficacy and safety of selumetinib in patients with NF1 were identified in PubMed and EMBASE up to January 28, 2021. The pooled objective response rates (ORRs) and disease control rates (DCRs) were calculated using the DerSimonian–Laird method based on random-effects modelling. The pooled proportion of adverse events (AEs) was also calculated. The quality of the evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation system.
Results of the study are:
Five studies involving 126 patients were included in our analysis. The studies had a very low to moderate quality of the evidence. The pooled ORR was 73.8% (95% CI 57.3%–85.5%) and the DCR was 92.5% (95% CI 66.5%–98.7%). The 2 most common AEs were diarrhoea, which had a pooled rate of 63.8% (95% CI 52.9%–73.4%), and an increase in creatine kinase levels, which had a pooled rate of 63.3% (95% CI 35.6%–84.3%).
Their results indicate that selumetinib is an effective and safe treatment for pediatric patients with symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas. Further larger-scale randomized controlled studies are needed to confirm the long-term outcome of patients treated with this drug.
Reference:
Efficacy and Safety of Selumetinib in Pediatric Patients With Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis by Jisun Hwang, et al. published in the Neurology.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


