- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Skin biopsy helpful in patients with suspected meningococcal Purpura Fulminans
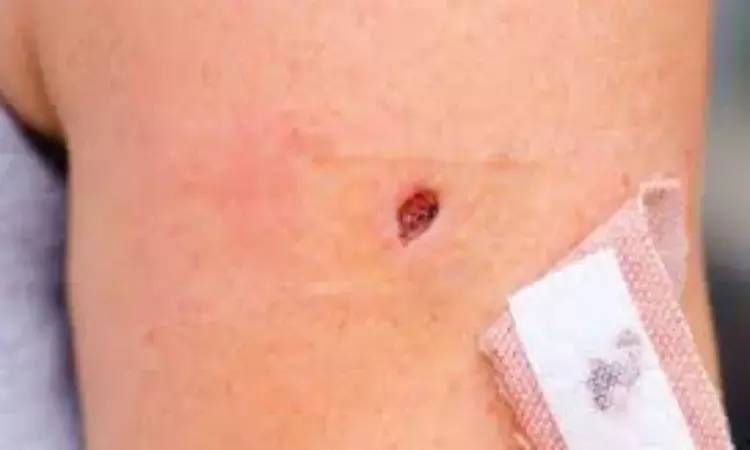
France: Skin biopsy with conventional culture and meningococcal PCR should be systematically considered in case of suspected meningococcal PF (Purpura Fulminans) to increase the diagnostic work-up, even after initiating antimicrobial treatment, a recent study has shown.
In the 17-year multicenter retrospective cohort study published in Critical Care, skin biopsy with conventional culture and meningococcal PCR was shown to have a global sensitivity of 88%.
Purpura fulminans is a rare infectious disease having high morbidity and mortality, with 41% deaths in the ICU and 28% of the survivors needing limb amputations with a median number of three amputated limbs. Neisseria meningitidis is the leading responsible bacteria of Purpura Fulminans, accounting for 66% of PF cases.
Skin biopsy is a minimally invasive and simple exam allowing to perform PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and skin culture to detect Neisseria meningitidis. Therefore, Damien Contou and the research team from France aimed to assess skin biopsy sensitivity in adult meningococcal PF patients.
The study included adult patients admitted to the ICU (intensive care unit) for a meningococcal Purpura Fulminans in whom a skin biopsy with conventional and meningococcal PCR was performed.
The study revealed the following findings:
· Among 306 patients admitted for PF, 64% had meningococcal PF, with a skin biopsy performed on 35%.
· Skin biopsy was performed in the median one day after initiating antibiotic therapy.
· In 90% of patients, a standard skin biopsy culture was performed and showed Neisseria meningitidis in 46% of them.
· Neisseria meningitidis PCR on skin biopsy was conducted in 75% of patients and was positive in 98%. Five of these 50 positive meningococcal PCR were performed three days or more after initiating antibiotic therapy.
· Skin biopsy was considered contributive in 88% of patients. The meningococcal serogroup was identified with skin biopsy in 71% of patients.
The study indicates that only 33% of meningococcal PF patients had a skin biopsy conducted. Skin biopsy is contributive in most patients with meningococcal PF, mainly when a meningococcal PCR is performed (up to 3 days following antibiotic therapy initiation).
Skin biopsy with meningococcal PCR and conventional culture has a global sensitivity of 88%.
"Given the PCR's high rentability versus the conventional culture, meningococcal PCR on skin biopsy should be considered in patients with suspected meningococcal PF, even several days after the antibiotic therapy initiation," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Contou, D., Béduneau, G., Rabault, C. et al. Skin biopsy in adult patients with meningococcal purpura fulminans: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Crit Care 27, 166 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04461-2
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


