- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Surgery best option for treating nodular primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis, states research
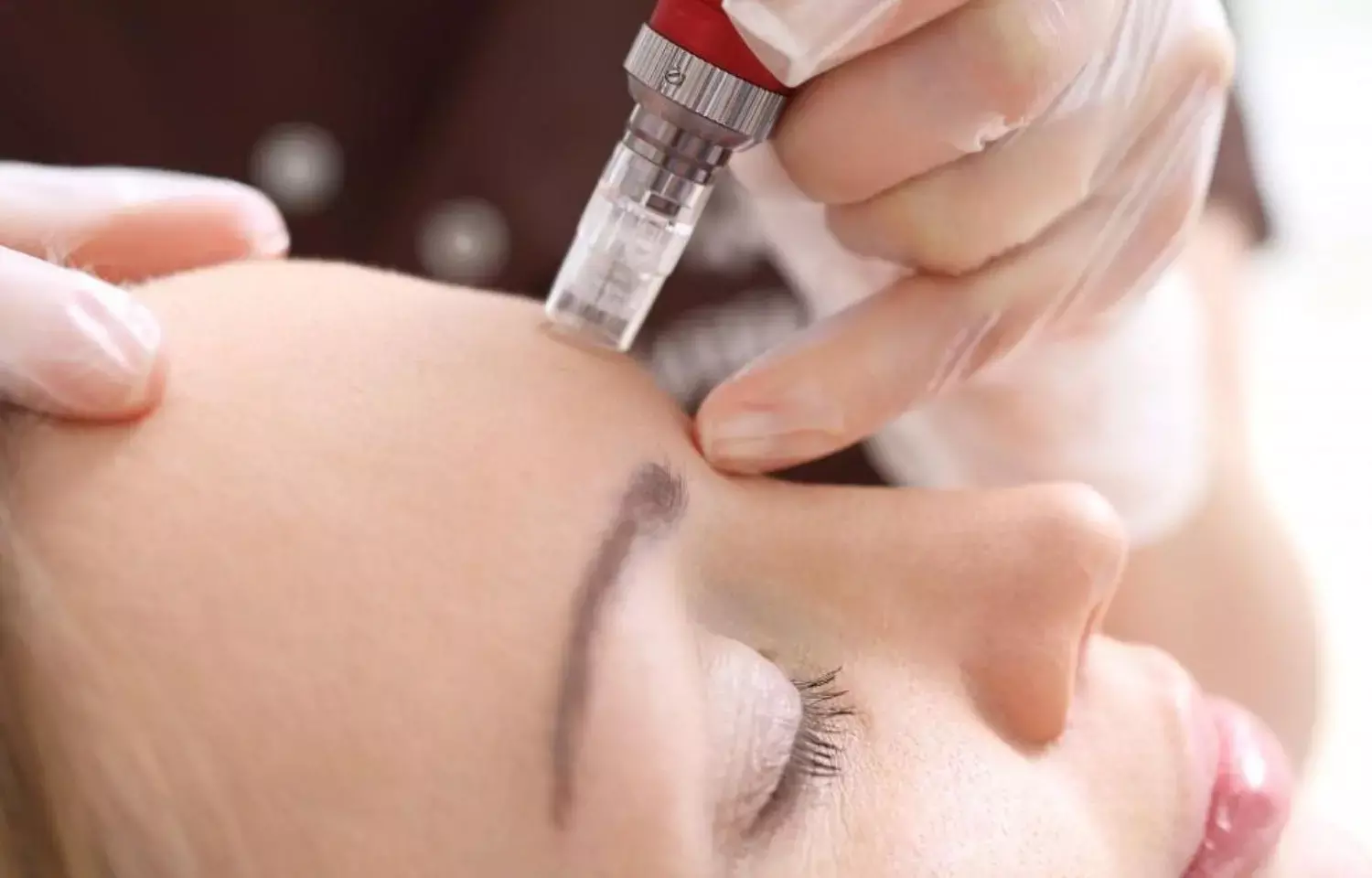
A new study published in the journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology showed that for non-nodular primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis (PLCA), laser therapy is recommended, but surgery is the most effective treatment for nodular amyloidosis.
Amyloid buildup in the dermis without systemic involvement is the hallmark of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis which is an uncommon skin condition. Instead of coming from immunoglobulin or serum protein deposits as in systemic types of amyloidosis, amyloid in PLCA is formed from the keratin peptides of necrotic keratinocytes.
Amyloid development in the skin is thought to be caused by the deposition of filamentous material as a result of severe scratching brought on by pruritogenic processes. Atopic dermatitis is one condition where chronic scratching can lead to keratinocyte destruction and localized amyloid development. This study was set to review the existing treatment approaches and to offer a modern viewpoint on PLCA therapy.
This study examined the Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and PubMed databases for relevant articles. While case reports and case series were assessed using the Mann-Whitney U test, cohort studies were meta-analyzed using a random effects model to assess the results of various therapies.
In all, a total of 535 patients from 117 trials were included. With statistically significant differences for the other treatments, surgery was the preferred treatment for nodular amyloidosis (NA). 20 cohort studies (418 patients) and 62 case-level studies (79 patients) were examined independently for the non-NA group. Biological medicines and JAK inhibitors may be viable treatment for refractory lesions, despite the fact that the case-level studies did not find any statistically significant differences between regimens.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, topical therapies, laser therapies, micro-needling, and systemic immunosuppressants had partial response (PR) rates of 100.0%, 100.0%, 97.5%, 96.9%, and 94.4%, respectively, while surgical procedures and laser therapies had complete response (CR) rates of 22.2% and 2.5%.
Overall, the study found surgery to be the best course of action for NA individuals, whereas laser treatment is advised for non-NA patients. For lesions that do not improve with traditional treatments, biologic medicines and JAK inhibitors could be interesting alternatives. JAK inhibitors and biological agents offer potential for refractory lesions. Also, a 100% partial response rate was obtained using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and micro-needling which demonstrated a range of PLCA therapy alternatives.
Source:
Wang, Q.-X., Ye, Q., Zhou, K.-Y., Luo, S.-Y., & Fang, S. (2025). A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatments and outcomes of primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1093/ced/llaf081
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


