- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
T lanceolata leaf extract may improve stretch marks in women, Finds study
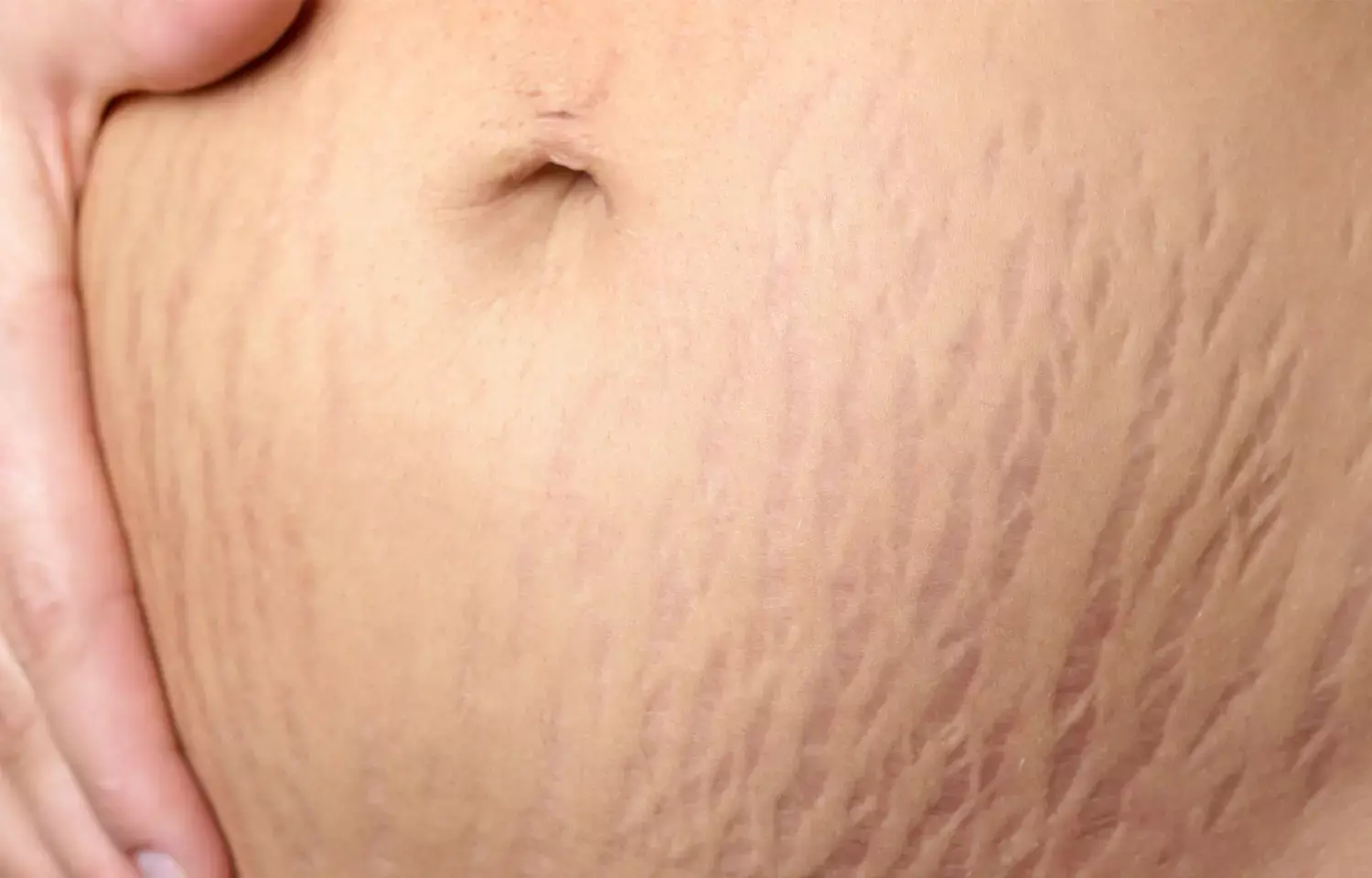
In recent research, investigators have deduced that Tasmannia lanceolata leaf extract alleviates stretch mark appearance in women and stimulates extracellular matrix synthesis in ex vivo human skin explants.
The study is published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
The leaves of Tasmannia lanceolata mainly contain polygodial that is known to exhibit a range of biological functions including anti‐inflammatory effects.
Therefore, Emmanuelle Gaillard and associates from the Robertet Group, Grasse, France conducted studies aimed to assess the effects of Tasmannia lanceolata extract (TLE) on the skin and more particularly on the stretch marks in women.
They carried out a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical study on 29 women, aged from 25 to 60 years, to investigate the effects of TLE on stabilized stretch marks. TLE and placebo products were topically applied daily for 8 weeks. 2D and 3D photograph processing was used to assess the skin roughness and firmness of stretch marks and further subjected to analysis.
Dermal density and thickness were evaluated using ultrasound, while stretch mark conditions (length, color, and depth) were determined by clinical scoring. Matricial proteins (pro‐collagen I and elastin) and pro‐matricial factors, like TGF‐β concentrations, were quantified from cultures of human skin explants presenting stretch marks, treated with TLE or vehicle control.
The following findings were noted-
a. Skin roughness of stretch marks was significantly reduced in the TLE group after 8 weeks of treatment.
b. Skin firmness of stretch marks was significantly increased in the TLE group after 4 weeks of treatment and this improved effect was maintained until the end of the study.
c. Dermal density and thickness were significantly increased in the TLE group compared to the placebo group.
d. Furthermore, TLE restored the dermal condition of the stretch mark skin, up to normal skin levels.
e. In addition, pro‐collagen I and elastin concentrations were found to be higher in the TLE‐treated stretch mark skin explants compared to the untreated ones, associated with higher quantities of TGF‐β production.
These results revealed that TLE could help improve the aspect of stabilized stretch marks in women by restoring the matricial environment, the authors concluded.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


