- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Targeting type I interferons may control inflammation in psoriasis patients: Study
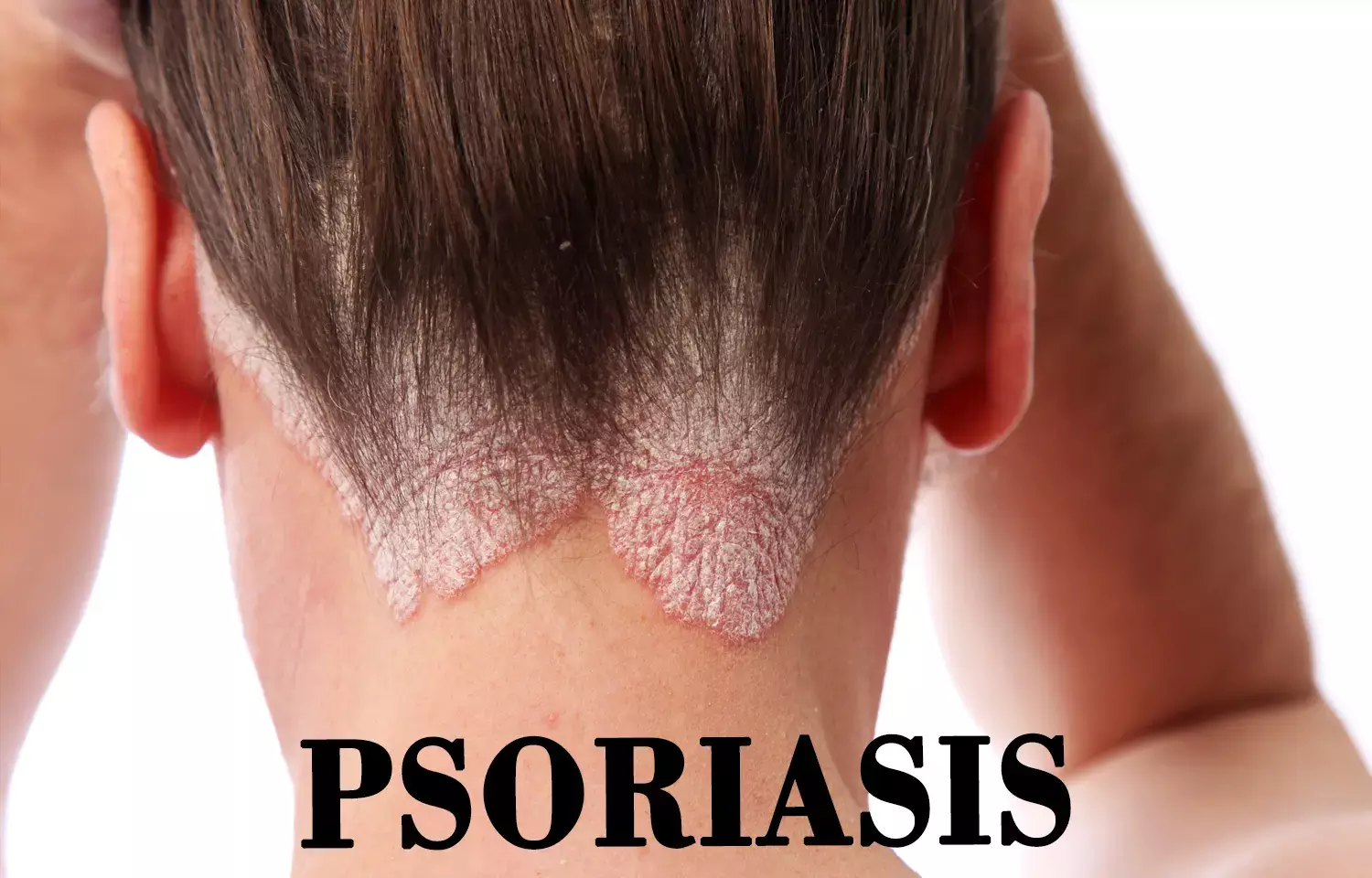
The findings suggest that using therapies to modulate interferon states may limit inflammation in psoriasis patients. Michigan: According to a recent study, targeting a type of skin protein called interferon kappa may reduce the severity of psoriasis by controlling inflammation.
In the study, published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, the researchers by using a model that mimics psoriasis in mice found that changing the levels of interferon kappa, a protein made by skin cells, altered the severity of inflammation and production of cell signaling molecules, called cytokines, that induce inflammation characteristic of psoriasis. Investigators found more psoriasis-like inflammation when more interferon kappa was present, while decreasing interferon kappa levels reduced disease.
Interferons play a major role in activating the body's response to viral threats, but they have also been detected in the lesions of many psoriasis patients at abnormal levels. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes the overproduction of skin cells and impacts nearly 30 million people in the world.
"We've known that psoriatic inflammation is marked by interferon-related gene expression, but how interferons alter the severity of the disease has not been clear," said J. Michelle Kahlenberg, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of rheumatology at Michigan Medicine and senior author of the paper. "Understanding how interferon kappa may modulate psoriasis brings us one step closer to optimizing our treatments."
The research team induced psoriasis in mouse models, splitting them into groups with interferon kappa at low, normal or elevated levels. The overexpressed protein alone didn't induce the disease, but it primed the skin for the inflammatory response that followed.
"This work shows how the context of the skin environment can shape inflammatory responses." said Mehrnaz Gharaee-Kermani, DVM, M.P.H., Ph.D., lead author of the study and a senior research lab specialist at Michigan Medicine. "It will be exciting to see how this can be applied in clinic."
The research team is conducting further studies to understand the role of interferon kappa in psoriasis patients through their Taubman Institute-sponsored study at Michigan Medicine and in partnership with Johann E. Gudhonsson, M.D., Ph.D., receiving funding through the National Psoriasis Foundation. Several treatments are used against the disease, but there is no cure.
A few current psoriasis drugs inhibit interferons, but many that are more specific are still in the trial phase. Coupled with the study's findings, personalized medicine will be paramount as physicians attempt to treat this disease, Kahlenberg said.
"Until now, treatments have been tested by studying a drug in hundreds of patients, lumping the average of them all together and targeting the average of those patients," Kahlenberg said. "As any patient who has been on these medications will tell you, this trial-and-error approach wastes patient time and money trying to get control of the disease. Understanding a patient's background level of interferon might help us target things within that person to make their disease better faster and stay in remission."
Reference:
The study titled, "Interferon Kappa Is a Rheostat for Development of Psoriasiform Inflammation," is published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
https://www.jidonline.org/article/S0022-202X(21)01452-4/fulltext
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


