- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Tildrakizumab therapy proves beneficial for Plaque Psoriasis
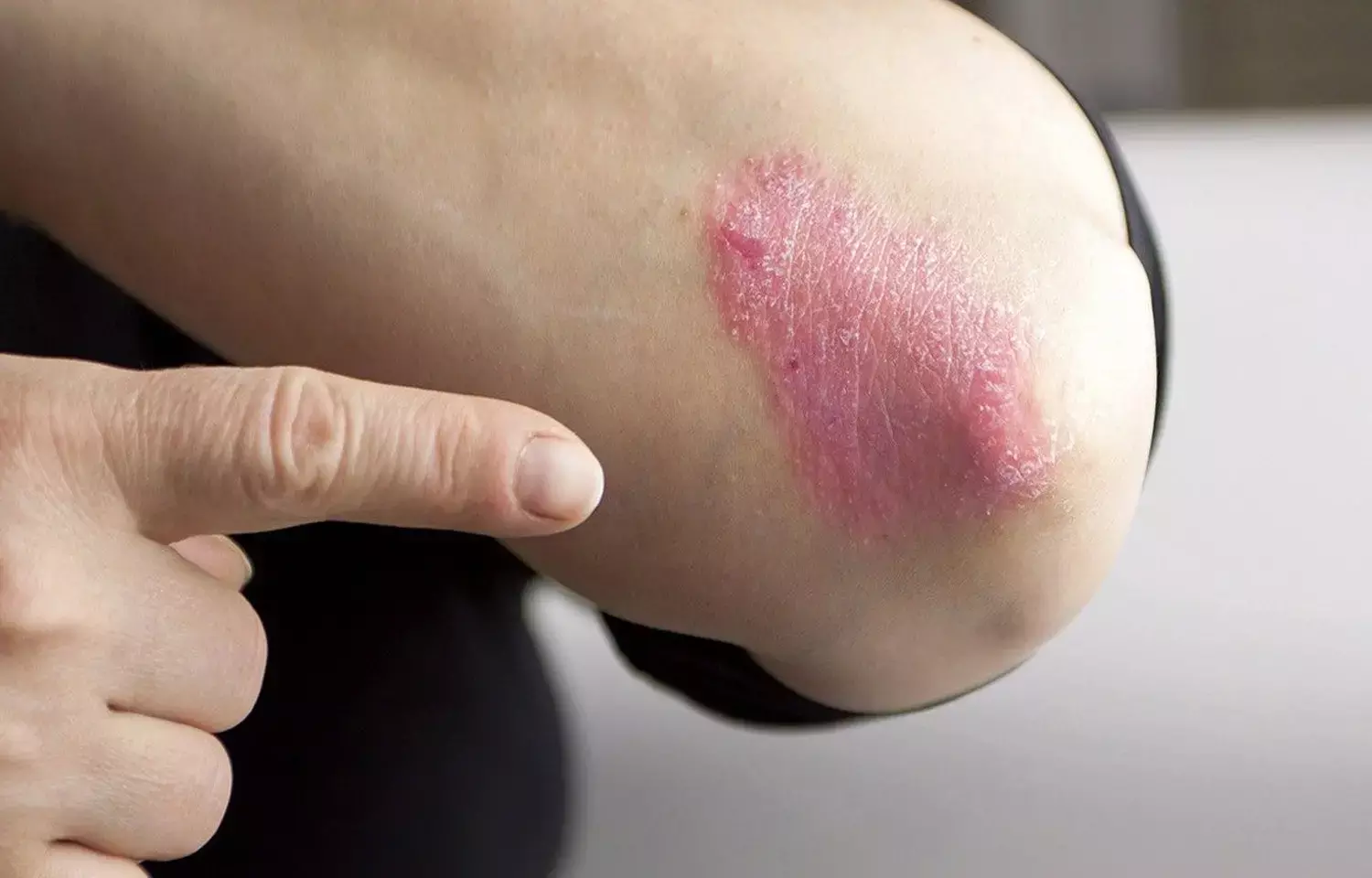
ITALY: Tildrakizumab was found to be beneficial for up to 36 weeks in treating moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, according to a new study published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Few biological therapies have proven to be well-tolerated, despite the fact that several effective ones have been established to treat plaque psoriasis. Prior to this investigation, the monoclonal antibody tildrakizumab was evaluated in two phase 3 trials and found to be both safe and efficacious. Real-world trials examining the effectiveness of tildrakizumab in moderate-to-severe psoriasis are not yet available.
The Department of Mental and Physical Health and Preventive Medicine at the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, under the direction of Drs. Alessio Gambardella and Gaetano Licata, built on those earlier studies by treating patients with additional comorbidities and altering other clinical traits.
In 30 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, the authors examined the effectiveness of tildrakizumab over a period of 36 weeks in a clinical setting.
A retrospective analysis with 30 people who had moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis was employed by the researchers (PsO). The individuals in the trial were administered 100 mg of tildrakizumab through subcutaneous injection at weeks 0, 4, and every 12 of the following weeks and then monitored for 36 weeks in a real-world environment. The majority of research participants had jobs; therefore, they could only visit the hospital once every 12 weeks. Having moderate-to-severe PsO with body surface area involvement of less than 10%, a Physician's Global Assessment (PGA) score of less than 3, and a Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of less than 12 were the main exclusion criteria for the enrolled subject. Furthermore, at least two conventional psoriasis treatments had to have been tried and failed, or the individuals had to have adverse effects or contraindications.
Key highlights of the study:
- The researchers discovered that after 12, 24, and 36 weeks in 86.7%, 100%, and 100% of patients, respectively, treated with tildrakizumab, participants' PASI scores of less than 3 were reported.
- Additionally, they discovered that PASI scores significantly dropped from 17.6 ± 4.7 at baseline to 4.7 ± 4.7 and 1.1 ± 3.9 at 4 and 12 weeks, respectively, and remained below 1 up to 36 weeks (P < 0.001 against baseline). Furthermore, at 36 weeks, 100%, 96.7%, and 60% of individuals, respectively, attained PASI scores of 75, 90, and 100.
- According to the study's findings, the DLQI also considerably fell from the baseline value of 13.8±2.9 to 3.6 1±.6 by 4 weeks, 1.4 ±0.6 by 12 weeks, and 0 at weeks 24 and 36 (P <0.001 against baseline).
- Furthermore, a multivariate model analysis showed that the 4-week effect of tildrakizumab treatment on DLQI and PASI scores was unrelated to gender, age, disease duration, BMI, prior biologic, or the presence of comorbidities.
They stated that "Tildrakizumab was found to be efficacious and safe in real-life clinical practice up to 36 weeks in moderate-to-severe plaque PsO." The fact that this effect was unrelated to other predictive variables made it possible to deliver it to patients with a variety of clinical features, such as those who had received prior biological treatment and/or concomitant conditions.
REFERENCE
Gambardella, A, Licata, G, De Rosa, A, Calabrese, G, Alfano, R, Argenziano, G. Treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis with tildrakizumab in the real-life setting. JEADV Clin Pract. 2022; 1– 7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jvc2.65
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


