- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical cetirizine effective against androgenetic alopecia, study finds
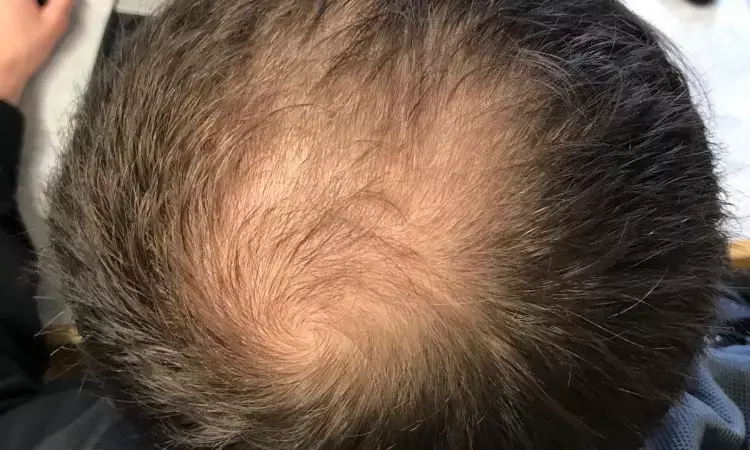
China: 1% topical cetirizine could be a choice for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia (AGA), particularly for those patients with a negative response to topical minoxidil, a recent study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology has revealed.
Cetirizine is an agent used widely for allergic disorders. It has been in use recently for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Ming Yang, Chinese Cochrane Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, and colleagues, therefore, aimed to summarize the current evidence regarding the effectiveness and safety of topical cetirizine for AGA treatment.
For this purpose, the researchers searched online databases. Both randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-randomized clinical trials were included. Initially, they identified 102 records, of which, two RCTs and one non-randomized clinical trial were included, which were of moderate-to-high risk of bias.
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
- All included trials used 1% topical cetirizine as the intervention with various regimens.
- Topical cetirizine was likely to be more effective than a placebo for treating AGA.
- In comparison with topical minoxidil, topical cetirizine appears to be less effective for improving total and vellus hair density, but it might have a longer-lasting effect.
- Cetirizine might be as effective as minoxidil in improving hair diameter.
The researchers wrote, "1% topical cetirizine may serve as a choice for treating AGA, particularly for patients with a negative response to topical minoxidil."
They further add that there is a requirement for additional well-designed RCTs in order to fully understand the role of topical cetirizine for AGA.
What is androgenetic alopecia?
Androgenetic alopecia is a common type of hair loss seen in both men and women. In men, this condition is also known as male-pattern baldness. Hair is lost in a well-defined pattern, beginning above both temples.
In women, the pattern of hair loss is different from male-pattern baldness. The hair becomes thinner all over the head, and there is no receding in the hairline. This condition rarely leads to total baldness in women.
Reference:
Chen X, Xiang H, Yang M. Topical Cetirizine for Treating Androgenetic Alopecia: A Systematic Review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Aug 17. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15309. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35976065.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


