- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical cetirizine shows higher clinical improvement for female androgenetic alopecia
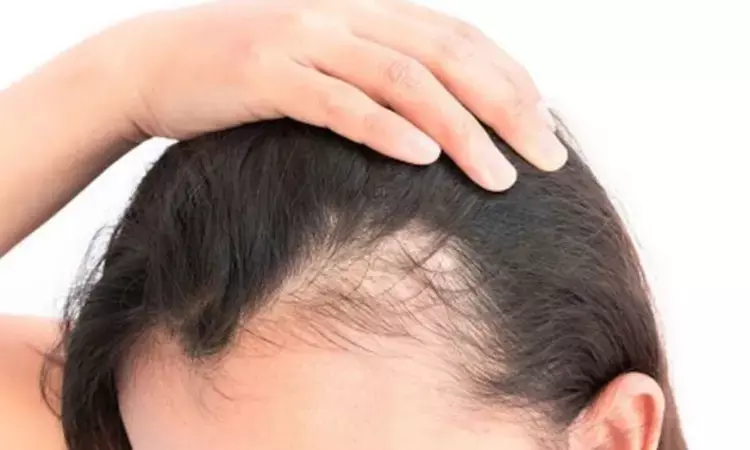
Egypt: A new study has claimed that topical cetirizine with minoxidil for treating female androgenetic alopecia led to the patient's perspective of more remarkable clinical improvement with a good safety profile and increased hair shaft thickness. The study's findings appeared in the Archives of Dermatological Research on 26th December 2022.
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most frequent cause of hair loss in both genders, with a higher psychological impact on females. Minoxidil currently is the only FDA-approved treatment for female androgenetic alopecia (FAGA), and it needs lifelong application and causes side effects. Prostaglandins (PGs) may play a role in hair growth, PGF and PGE increase hair growth, but prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) inhibits it, increases sebaceous hyperplasia, and is elevated in bald scalp. Cetirizine is an antihistamine that increases PGE, inhibits PGD2 and reduces inflammatory cell infiltrate, making it a potentially safe treatment for androgenetic alopecia.
In the randomized, double-blind, controlled, parallel study conducted at Dermatology Clinic, Cairo University Teaching Hospital, Egypt, Eglal A. Bassiouny and colleagues aimed to compare the safety and efficacy of topical cetirizine with minoxidil (group 1) versus s topical minoxidil with placebo (group 2) in female patients with androgenetic alopecia. "To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study on cetirizine as an add-on in female androgenetic alopecia," they wrote.
The study included sixty-six patients with female AGA aged 20-50 years, Sinclair (II–IV). The trichoscopic parameters, side effects, patients' self-assessment, and global photographic assessment were evaluated. They were randomly assigned to either group 1 or 2 for 24 weeks.
The authors reported the following findings:
· There was a statistically significant change from baseline in frontal and vertex terminal and vellus hair density with a significant increase in vertex hair shaft thickness and an average number of hairs per follicular unit in group 1.
· Patients reported significantly better scores in patient self-assessment in group 1.
· Side effects were not significantly different between groups.
To conclude, cetirizine may lead to clinical improvement in FAGA and increases shaft thickness with no side effects making it a potential therapy for FAGA.
"Pharmacokinetic studies on dose-dependent hair growth and its bioavailability in follicular hair sheath are recommended along with studies to evaluate the drug's exact mechanism of action, the efficacy of its oral dosage form and other H1-blockers, and its effectiveness in other alopecia types," the researchers wrote. More studies are required to determine whether topical cetirizine alone or oral cetirizine is effective.
Reference:
Bassiouny, E.A., El-Samanoudy, S.I., Abbassi, M.M. et al. Comparison between topical cetirizine with minoxidil versus topical placebo with minoxidil in female androgenetic alopecia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Dermatol Res (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-022-02512-2
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


