- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Topical Timolol Found Safe and Well-Tolerated for Infantile Hemangioma: Study
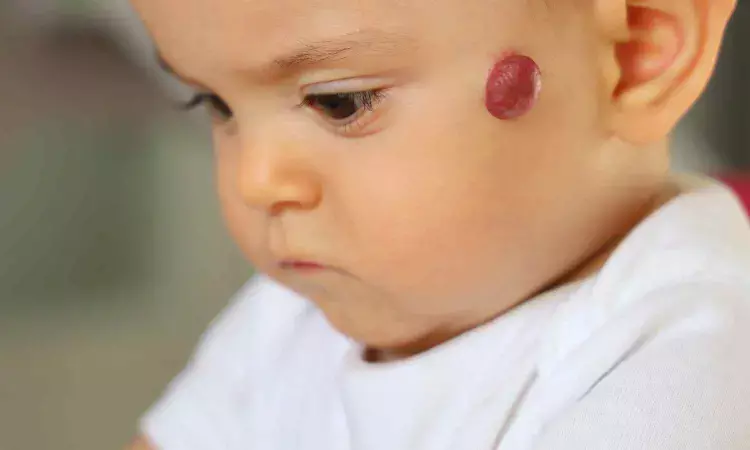
Topical timolol has been reported by researchers to be safe and well-tolerated for the treatment of infantile hemangioma (IH), according to a new study. The study concluded that although local irritation may occur in a small number of cases, serious systemic adverse effects are uncommon and confirm the favorable safety profile of this drug for use in infants. The study was published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology by Nicole W. and colleagues.
The present study was designed as a systematic review in line with the 2020 PRISMA guidelines. Researchers searched the PubMed and MEDLINE databases for studies published between 2000 and 2024 that reported specifically on adverse effects related to the use of topical timolol in infants with IH. A total of 20 studies met the inclusion criteria, including 1,780 patients in total who were treated with topical timolol for infantile hemangiomas. The data from these studies were analyzed to determine the frequency, type, and severity of both local and systemic side effects.
Results
• The results showed that topical timolol was generally well-tolerated, with 4.7% of treated patients exhibiting local adverse effects.
• These have included skin irritation, scaling, ulceration, and pruritus.
• Significantly, the majority of these local reactions are mild and self-limiting, with no need for the discontinuation of therapy.
• Systemic adverse effects were exceedingly uncommon, occurring in only 1.2% of patients.
• The systemic effects reported included bradycardia, bronchospasm, wheezing, hypothermia, and disturbances of sleep.
• No life-threatening reactions were noted, and no consistent pattern emerged that would indicate that local irritation predisposes infants to systemic absorption or complications.
• Moreover, no relationship was observed between duration of treatment and systemic effects, indicating that prolonged use of topical timolol per se did not constitute a risk factor.
• It was also noted by researchers that preterm infants and those with ulcerated or deep hemangiomas might be more predisposed to systemic absorption, although evidence for this may be limited.
This comprehensive review of 1,780 patients in 20 studies confirmed the general safety and good tolerance of topical timolol in the management of infantile hemangioma, with systemic side effects in only 1.2% and local irritation in 4.7%. Researchers emphasized that further investigation is necessary to refine dosing protocols and identify patient-specific risk factors to ensure the continued safe use of topical timolol in infants worldwide.
Reference:
Werpachowski, Nicole & Susla, Lyudmyla & Lal, Karan. (2025). Complications of Topical Timolol in the Management of Infantile Hemangiomas: A Systematic Review. 10.13140/RG.2.2.27885.91367.
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


