- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Upadacitinib useful option for managing Atopic dermatitis with concomitant hand eczema
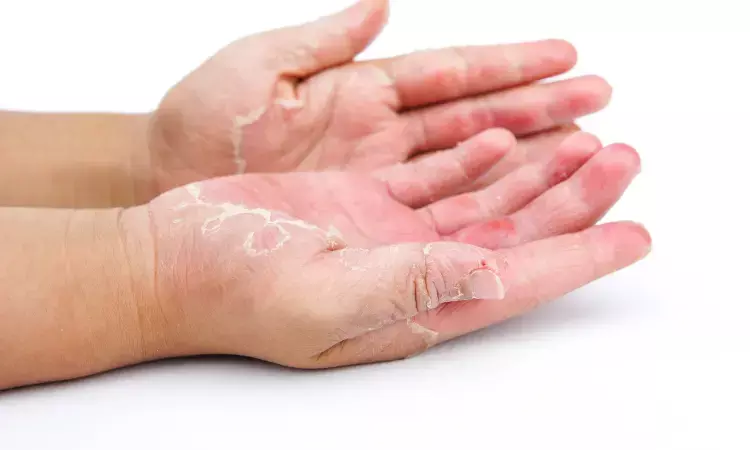
Netherlands: Research published in Contact Dermatitis, has concluded that, in daily practice, Upadacitinib is an effective treatment for Atopic Dermatitis (AD) patients and concomitant hand eczema (HE).
AD and HE are prevalent inflammatory skin disorders. 50% of AD patients present with hand involvement and have a fourfold increased lifetime prevalence of HE compared to individuals without AD.
The HE subtypes are irritant contact dermatitis (ICD), allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) and protein contact dermatitis (PCD). There are limited treatment options for HE patients.
Newer AD treatments have been developed. Dupilumab is effective for treating HE in AD patients. Other recently available systemic treatments for AD include Janus Kinase (JAK)-inhibitors which could effectively treat HE irrespective of the subtype.
Daily practice data on upadacitinib's effectiveness in AD is promising, but the data is limited. Few case series and reports have been published in this context.
Considering this, Esmé Kamphuis et al with team evaluated the 16-week effectiveness and safety of upadacitinib on AD and HE in AD patients.
The study summary includes the following:
The cohort study had clinical outcomes: (at baseline week four and week 16)
Eczema Area and Index: HECSI
Photographic guide
PROMs: average pruritus and pain
Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) score
Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM)
Patient-Oriented Eczema
Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)
Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool (ADCT)
Patient Global Assessment of Disease (PGAD)
Quality Of Life Hand Eczema Questionnaire (QOLHEQ).
- The study included 38 patients.
- Thirty-two patients had Hand Eczema.
- EASI-75 was achieved by 50.0% at week 16.
- The researchers reported 62.5% of patients with an absolute cutoff score of ≤4 on the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), 37.5% had a Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) of ≤7, and 59.4% of patients had ≤5 scores on the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI).
- 68.8 % of patients had ADCT <7
- 53.1 % of patients had a 'good' PGAD rating.
- 59 % of patients achieved HECSI-75, and 74.1 % achieved a clear photographic guide.
- The minimally important change in QOLHEQ was achieved by 57.9%.
- Sub-analysis with concomitant irritant contact dermatitis patients showed no differences.
- No new findings in safety analysis were reported.
To conclude, Upadacitinib can be an effective treatment strategy for AD patients.
There was marked improvement of HE in patients treated with upadacitinib for AD.
Future studies are warranted to investigate the effect on the different etiological subtypes of HE.
Kamphuis, Esmé, et al. "Experiences From Daily Practice of Upadacitinib Treatment on Atopic Dermatitis With a Focus on Hand Eczema: Results From the BioDay Registry." Contact Dermatitis, Wiley, Jan. 2023. Crossref, https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.14276.
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


