- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
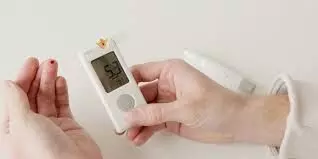
Antidepressant Use linked to Insulin Initiation in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with depression

In a groundbreaking investigation, researchers have delved into the intricate relationship between antidepressant prescribing and the initiation of insulin therapy in individuals battling both depression and type 2 diabetes. The study underscores the robust association between antidepressant prescribing and the initiation of insulin therapy in individuals with comorbid depression and type 2 diabetes.
The study results were published in the journal Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.
Approximately 25% of individuals with type 2 diabetes experience comorbid depression, impacting glycemic control and diabetic complications. Depression symptoms hinder self-care, and adherence to treatments, and promote unhealthy behaviors. Antidepressant medications, recommended for moderate to severe depression, show short-term efficacy in improving depression and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. As existing studies were inconclusive, researchers conducted a study to investigate the link between antidepressant prescribing and insulin initiation in type 2 diabetes and comorbid depression, hypothesizing that antidepressant use may decrease insulin initiation rates, positively impacting diabetic health and self-care.
Conducted using UK primary care records, this nested case-control study sheds light on a significant association that could potentially reshape our understanding of the interplay between mental health and diabetes management.
Leveraging the extensive dataset from UK primary care records, the study adopted a nested case-control design. Cases were identified as those initiating insulin, while controls were individuals maintaining their diabetes management through oral antidiabetic medications. The analysis employed advanced statistical techniques, including conditional logistic regression, to estimate incident rate ratios (IRRs) with 95% confidence intervals, adjusting for key factors such as demographic characteristics, comorbidities, health service utilization, and prior medication history.
Key Findings:
The study encompassed a substantial cohort, including 11,862 cases initiating insulin and 43,452 controls.
The findings revealed a striking association between antidepressant prescribing and insulin initiation.
Any antidepressant prescription was linked to a noteworthy incident rate ratio (IRR) of 3.78 (95% CI 3.53–4.04).
Prolonged durations (24+ months) of antidepressant treatment exhibited a significantly higher IRR of 5.61 (95% CI 5.23–6.03).
The prescription of a greater number (3+) of different antidepressant agents resulted in a remarkable IRR of 5.72 (95% CI 5.25–6.24).
Surprisingly, the study did not observe a substantial difference between recent and non-recent antidepressant prescriptions or among various antidepressant agents.
The study's groundbreaking findings highlight a robust connection between antidepressant prescribing and the initiation of insulin therapy in individuals grappling with comorbid depression and type 2 diabetes. However, researchers caution against interpreting this association as a direct causal effect of antidepressant medication. Instead, it could serve as a potential marker, indicating more severe depression influencing diabetic control.
This calls for a nuanced understanding of the intricate relationship between mental health treatments and diabetes management, urging a holistic approach to address the multifaceted challenges faced by individuals with type 2 diabetes and comorbid depression. As researchers delve deeper into this complex interplay, these findings may pave the way for more tailored and comprehensive treatment strategies in the future.
Further reading: Jeffery A, Walters K, Wong ICK, Osborn D, Hayes JF. The association between antidepressant treatment and rates of insulin initiation in comorbid depression and type 2 diabetes: A UK electronic health record nested case-control study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Published online December 28, 2023. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.111083
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751